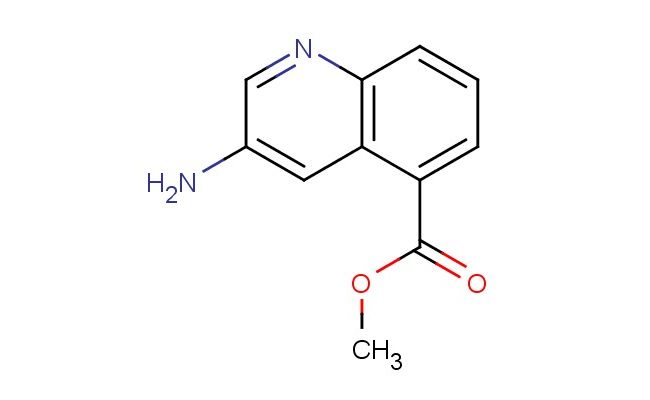
methyl 3-aminoquinoline-5-carboxylate
$300.00
CAS No.: 1956382-58-3
Catalog No.: 191955
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H10N2O2
MW: 202.213
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C=NC=2C=CC=C(C2C1)C(=O)OC
Catalog No.: 191955
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H10N2O2
MW: 202.213
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C=NC=2C=CC=C(C2C1)C(=O)OC
methyl 3-aminoquinoline-5-carboxylate; CAS No.: 1956382-58-3; methyl 3-aminoquinoline-5-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: Methyl 3-aminoquinoline-5-carboxylate (CAS No.: 1956382-58-3) appears as a pale yellow crystalline powder with a slight ester odor. The compound features an amino group at position 3 and a methyl ester at position 5 of the quinoline ring system. It demonstrates a melting point between 155-158 C and exhibits moderate basicity due to the amine functionality, with a pKa value around 5.4. Solubility characteristics reveal good dissolvability in polar organic solvents such as ethyl acetate and dichloromethane, while being sparingly soluble in water due to the hydrophobic ester group. The substance is moisture-sensitive and prone to hydrolysis under acidic or basic conditions, necessitating storage in a tightly sealed container under nitrogen atmosphere at controlled room temperature (15-25 C). Safety precautions include using P295 respiratory protection, nitrile gloves, and safety goggles due to potential skin irritation and eye damage. The compound has a moderate vapor pressure and forms flammable mixtures with air above 45 C. APPLICATIONS: Methyl 3-aminoquinoline-5-carboxylate functions as a critical intermediate in developing anticancer agents targeting specific protein kinases as documented in oncology research. Its quinoline scaffold enables bioisosteric replacements in drug discovery, facilitating improved metabolic stability of lead compounds as reported in pharmaceutical chemistry literature. Additionally, 1956382-58-3 serves as a building block for fluorescent probes used in detecting specific nucleic acid sequences, with several studies highlighting its utility in creating molecular beacons for genetic diagnostics. The compound also contributes to the synthesis of agrochemical intermediates for developing herbicides with novel mechanisms of action, as described in agricultural chemistry literature.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review