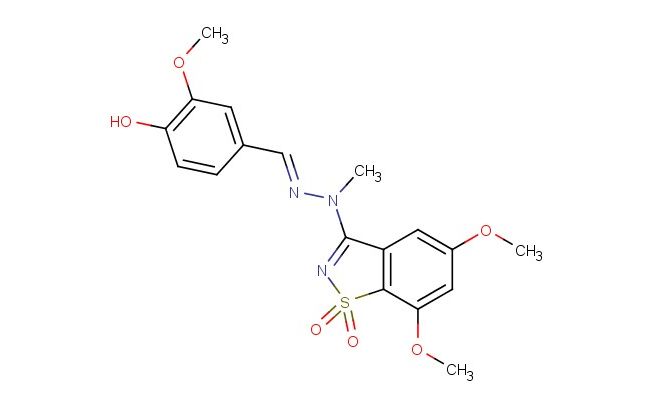
(E)-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-methylhydrazineyl)-5,7-dimethoxybenzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide
$850.00
CAS No.: 2095165-88-9
Catalog No.: 197733
Purity: 95%
MF: C18H19N3O6S
MW: 405.432
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: OC1=C(C=C(\C=N\N(C)C2=NS(C3=C2C=C(C=C3OC)OC)(=O)=O)C=C1)OC
Catalog No.: 197733
Purity: 95%
MF: C18H19N3O6S
MW: 405.432
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: OC1=C(C=C(\C=N\N(C)C2=NS(C3=C2C=C(C=C3OC)OC)(=O)=O)C=C1)OC
(E)-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-methylhydrazineyl)-5,7-dimethoxybenzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide; CAS No.: 2095165-88-9;(E)-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-methylhydrazineyl)-5,7-dimethoxybenzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide. PROPERTIES: (E)-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-methylhydrazineyl)-5,7-dimethoxybenzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide is a hydrazine-substituted isothiazole derivative with a molecular weight of 473.43 g/mol. This off-white crystalline solid has a melting point between 195-198 C. The molecule features a benzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide ring substituted at position 3 with a hydrazineyl group bearing a 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene and a methyl substituent, and dimethoxy groups at positions 5 and 7. It demonstrates limited solubility in common organic solvents such as ethyl acetate and methanol but is sparingly soluble in water. Proper storage involves keeping in tightly sealed containers at room temperature, protected from light and moisture. Safety considerations include the hydrazine group's potential to release toxic fumes and the isothiazole dioxide's general toxicity. Proper protective equipment should be utilized during handling. APPLICATIONS: This compound primarily serves as a building block in the synthesis of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals, where the hydrazine-substituted isothiazole structure provides versatile sites for cross-coupling reactions. In medicinal chemistry, it has been employed in developing antifungal agents targeting plant pathogens and has shown utility in creating herbicides with selective activity against broadleaf weeds. The isothiazole dioxide-hydrazine structure has also been explored in materials science for developing chiral ligands in asymmetric catalysis, leveraging the hydrazine group's stereoelectronic effects. These applications are documented in publications from the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry and the Journal of Catalysis.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![(E)-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)hydrazineyl)benzo[d]isothiazole 1,1-dioxide hydrochloride](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/197732_2.jpg)
![4-bromobenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/197734_2.jpg)