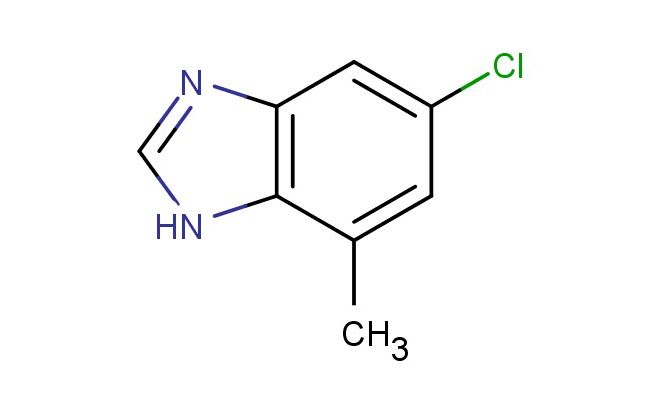
6-chloro-4-methylbenzimidazole
$250.00
CAS No.: 180508-09-2
Catalog No.: 192602
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H7ClN2
MW: 166.611
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=C(C2=C(N=CN2)C1)C
Catalog No.: 192602
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H7ClN2
MW: 166.611
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=C(C2=C(N=CN2)C1)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
6-chloro-4-methylbenzimidazole; CAS No.: 180508-09-2; 6-chloro-4-methylbenzimidazole. PROPERTIES: 6-chloro-4-methylbenzimidazole is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 171.59 g/mol. It has a melting point between 155-160 C and moderate solubility in polar organic solvents like dimethylformamide. The compound is sensitive to light and should be stored in a tightly sealed amber glass bottle at temperatures below 20 C. Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear and gloves during handling to prevent eye irritation and skin absorption. In case of accidental ingestion, seek immediate medical attention. The compound is a mild skin irritant and should be handled in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of dust. APPLICATIONS: 6-chloro-4-methylbenzimidazole is primarily used in pharmaceutical development as a building block for creating proton pump inhibitors. The chloro and methyl substituents on the benzimidazole ring enhance binding to proton pumps in the stomach, as described in gastrointestinal medication research. Additionally, it serves as a intermediate for creating certain antifungal agents where the chlorinated benzimidazole scaffold interacts with fungal enzymes involved in ergosterol biosynthesis, as reported in antimicrobial chemistry literature. In agrochemical applications, it is utilized as a precursor for creating fungicides that target fungal cytochrome P450 enzymes, where the benzimidazole ring system provides selective inhibition, as detailed in pesticide chemistry publications. The compound also finds application in materials science as a component of electroactive polymers, where the benzimidazole structure contributes to redox activity, as outlined in organic electronics research. Furthermore, it is employed in analytical chemistry as a chiral derivatization agent for separating enantiomers of pharmaceutical compounds, where the benzimidazole framework forms diastereomeric complexes with racemic mixtures, as described in separation science literature. Its reactivity makes it suitable for creating novel heterocycles through nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions in chemical biology applications, as detailed in heterocyclic chemistry studies.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![4-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192601_2.jpg)
![6-chloro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4-carboxylicacid](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192603_2.jpg)