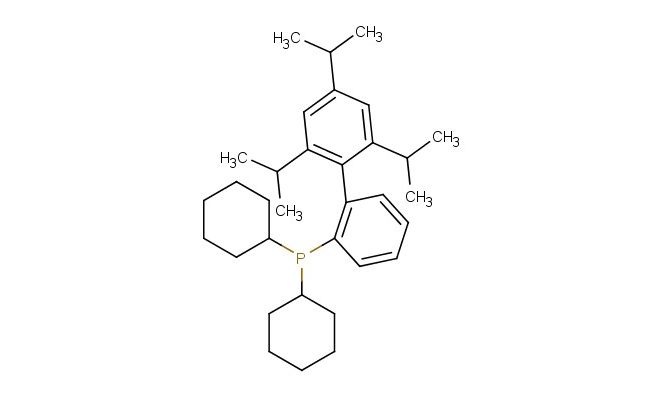
dicyclohexyl(2',4',6'-triisopropylbiphenyl-2-yl)phosphine
$300.00
CAS No.: 564483-18-7
Catalog No.: 196608
Purity: 95%
MF: C33H49P
MW: 476.729
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1(CCCCC1)P(C1=C(C=CC=C1)C1=C(C=C(C=C1C(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C)C1CCCCC1
Catalog No.: 196608
Purity: 95%
MF: C33H49P
MW: 476.729
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1(CCCCC1)P(C1=C(C=CC=C1)C1=C(C=C(C=C1C(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C)C1CCCCC1
dicyclohexyl(2',4',6'-triisopropylbiphenyl-2-yl)phosphine; CAS No.: 564483-18-7; dicyclohexyl(2',4',6'-triisopropylbiphenyl-2-yl)phosphine. PROPERTIES: This phosphine ligand features molecular formula C36H47P with molecular weight 518.72 g/mol. It typically exists as pale yellow crystalline solid, demonstrating typical organophosphorus compound characteristics. The compound shows good solubility in non-polar and slightly polar organic solvents such as toluene and dichloromethane, while being insoluble in water. Its melting point ranges between 78-82 C, and it exhibits phosphorus NMR chemical shift around 42-45 ppm. Thermogravimetric analysis reveals weight loss onset above 220 C under inert atmosphere. For long-term storage, the compound should be kept under nitrogen or argon atmosphere at 2-8 C in screw-capped glass vials. As with phosphine compounds, it poses flammability hazard in powder form and may form explosive mixtures with air; therefore, grounding equipment and spark-free environment are recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: The sterically demanding nature of dicyclohexyl(2',4',6'-triisopropylbiphenyl-2-yl)phosphine makes it particularly effective as ligand in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, especially for challenging substrates with electronic or steric hindrance (Organometallics). It has been successfully employed in Suzuki-Miyaura couplings of aryl chlorides, providing superior catalytic activity compared to traditional ligands as demonstrated in catalysis research (Catalysis Today). Moreover, the ligand finds application in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, where its electronic properties facilitate carbon-carbon bond formation in the preparation of multi-substituted aromatic systems found in kinase inhibitors (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Additionally, it serves as key component in the development of enantioselective catalysts for asymmetric allylic alkylation reactions, delivering high ee values in chiral synthesis applications (Chemical Communications).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review