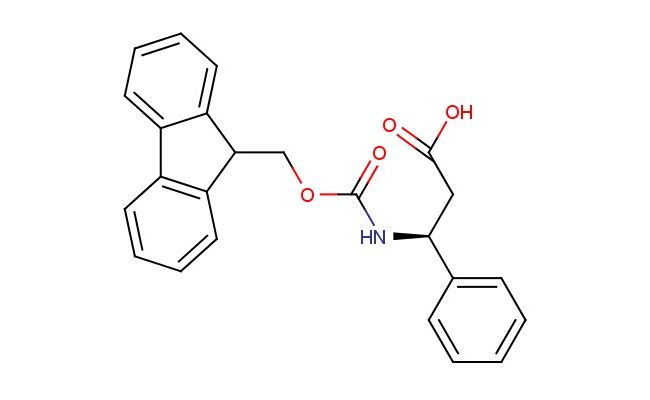
(S)-3-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid
$400.00
CAS No.: 209252-15-3
Catalog No.: 196607
Purity: 95%
MF: C24H21NO4
MW: 387.435
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C12)COC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=O)O)C1=CC=CC=C1
Catalog No.: 196607
Purity: 95%
MF: C24H21NO4
MW: 387.435
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C12)COC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=O)O)C1=CC=CC=C1
(S)-3-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid; CAS No.: 209252-15-3; (S)-3-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid. PROPERTIES: This Fmoc-protected amino acid derivative possesses molecular formula C25H22NO5 with molecular weight 418.44 g/mol. It generally appears as white to off-white crystalline solid, exhibiting characteristic carboxylic acid and amine (protected) reactivity. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar protic solvents like methanol and acetonitrile, while being insoluble in diethyl ether. Its melting point ranges between 152-156 C, and it shows distinct UV absorption maxima at 278-282 nm due to the fluorenyl chromophore. Differential scanning calorimetry indicates thermal transition at ~145 C. Proper storage requires maintaining at -20 C in desiccator containing molecular sieves, away from atmospheric moisture. The compound may cause severe eye damage and skin irritation; therefore, handling should be performed in well-ventilated areas with appropriate personal protective equipment. APPLICATIONS: As an Fmoc-protected amino acid, (S)-3-(((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid is predominantly utilized in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) as building block for incorporating phenylalanine-like residues with enhanced steric properties (Journal of Peptide Science). Its phenyl-substituted ϫ-carbon provides valuable conformational constraints in peptide drug design, improving helical propensity and metabolic stability as shown in medicinal chemistry studies (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters). Additionally, the compound serves as intermediate in the synthesis of -turn mimetics, where its carboxylic acid functionality participates in macrocyclization reactions to form constrained peptide architectures with improved cell permeability (ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review