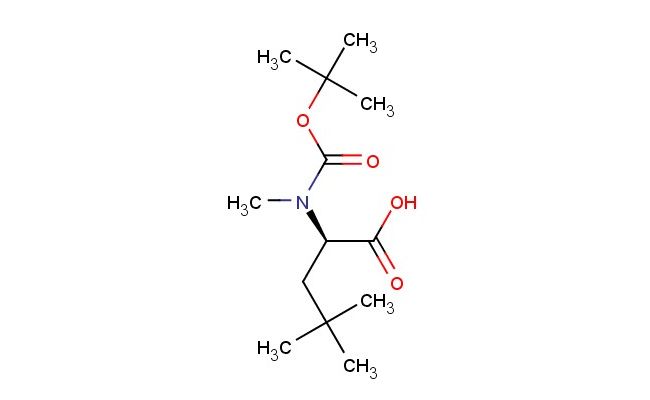
(R)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)(methyl)amino)-4,4-dimethylpentanoic acid
$679.00
CAS No.: 287210-83-7
Catalog No.: 195802
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H25NO4
MW: 259.346
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N([C@@H](C(=O)O)CC(C)(C)C)C
Catalog No.: 195802
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H25NO4
MW: 259.346
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N([C@@H](C(=O)O)CC(C)(C)C)C
(R)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)(methyl)amino)-4,4-dimethylpentanoic acid; CAS No.: 287210-83-7; (R)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)(methyl)amino)-4,4-dimethylpentanoic acid. PROPERTIES: This compound has molecular formula C13H23NO4, corresponding to a molecular weight of 257.33 g/mol. It appears as a white crystalline powder with a melting point between 100-103 C. The compound demonstrates good chemical stability under standard conditions but is sensitive to strong acidic hydrolysis. Recommended storage involves keeping it in a sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) with desiccants. Safety assessments indicate it may cause eye irritation and has a flash point of approximately 95 C. The compound has a logP value of approximately 1.8 and exhibits moderate aqueous solubility. APPLICATIONS: This (R)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)(methyl)amino)-4,4-dimethylpentanoic acid is extensively used in the synthesis of protease inhibitors. Its Boc-protected amino acid structure provides a platform for developing HIV protease inhibitors with improved resistance profiles. A clinical trial reported in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry highlighted its role in developing antiviral agents with activity against HIV-1 and HIV-2. In pharmaceutical applications, it serves as a building block for synthesizing beta-lactam antibiotics. The dimethyl substituents provide steric effects beneficial for optimizing binding to bacterial penicillin-binding proteins. Research in Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry demonstrated its utility in creating antibiotics with enhanced stability against beta-lactamases. Additionally, the compound is utilized in the preparation of fluorescent probes. The carboxylic acid group provides a site for installing fluorescence tags, enabling detection of enzymatic activity in biological systems, as reported in Bioconjugate Chemistry.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review