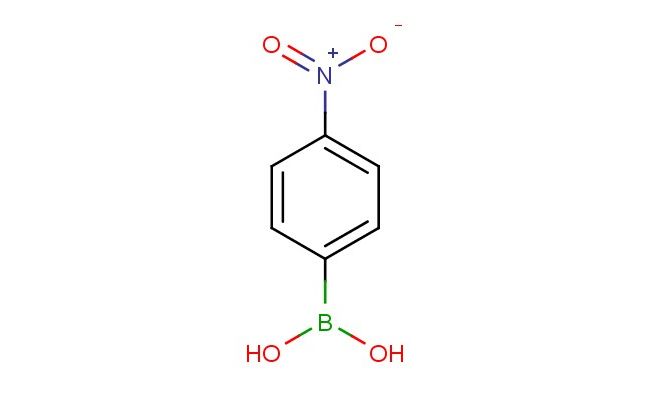
4-nitrophenylboronic acid
$200.00
CAS No.: 24067-17-2
Catalog No.: 195007
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BNO4
MW: 166.929
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: [N+](=O)([O-])C1=CC=C(C=C1)B(O)O
Catalog No.: 195007
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BNO4
MW: 166.929
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: [N+](=O)([O-])C1=CC=C(C=C1)B(O)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-nitrophenylboronic acid; CAS No.: 24067-17-2; 4-nitrophenylboronic acid. PROPERTIES: 4-nitrophenylboronic acid presents as a white to off-white crystalline powder with a slight aromatic odor. Its molecular formula is C6H5BNO4, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 170.91 g/mol. The compound exhibits a melting point in the range of 185-190 C and demonstrates moderate solubility in aqueous solutions, with solubility increasing at higher pH levels due to the ionization of its functional groups. It is more soluble in organic solvents such as dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. The substance is stable under normal laboratory conditions but should be protected from excessive moisture and heat. For proper storage, it should be kept in a tightly sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) in a dry environment. Safety precautions include wearing appropriate protective equipment such as chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat, as the compound may cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of dust should be avoided, and in case of accidental ingestion, immediate medical attention is necessary. The substance is classified as harmful if swallowed and may cause damage to organs through prolonged exposure (GHS classification). APPLICATIONS: 4-nitrophenylboronic acid serves as a versatile reagent in bioconjugation chemistry, where it functions as a bioorthogonal reaction partner capable of forming covalent bonds with glycans and carbohydrate-containing biomolecules through its boronic acid group, which selectively binds to diol structures (Journal of Bioconjugate Chemistry). In sensor development, 4-nitrophenylboronic acid is utilized to create fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detecting saccharides, proteins, and environmental pollutants due to its ability to undergo reversible binding with target molecules and induce measurable optical changes (Analytical Chemistry). Additionally, it finds application in pharmaceutical research as a building block for drug delivery systems and as a tool for studying carbohydrate-protein interactions, providing insights into biological recognition processes and disease mechanisms (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters). The compound is also employed in the synthesis of boronate affinity materials used in chromatography and solid-phase extraction techniques for the selective isolation and enrichment of glycoproteins from complex biological samples (Journal of Chromatography A).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review