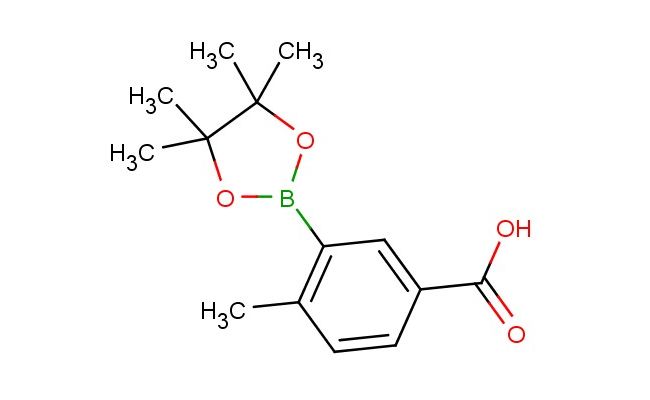
4-methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzoic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 515131-35-8
Catalog No.: 196621
Purity: 95%
MF: C14H19BO4
MW: 262.114
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C=C(C(=O)O)C=C1)B1OC(C(O1)(C)C)(C)C
Catalog No.: 196621
Purity: 95%
MF: C14H19BO4
MW: 262.114
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C=C(C(=O)O)C=C1)B1OC(C(O1)(C)C)(C)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzoic acid; CAS No.: 515131-35-8; 4-methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzoic acid. PROPERTIES: This boronate ester derivative possesses molecular formula C15H19BO4 with molecular weight 278.11 g/mol. It generally appears as off-white crystalline powder, exhibiting characteristic carboxylic acid and boronate ester functionalities. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar aprotic solvents like DMF and DMSO, while being sparingly soluble in ethyl acetate. Its melting point ranges between 138-142 C, and it shows distinct IR absorption bands corresponding to the boronate ester group (~1100-900 cm??) and aromatic C-H stretches. Differential scanning calorimetry reveals glass transition temperature around 65-70 C. Proper storage requires maintaining at 2-8 C in tightly sealed containers with desiccant, protected from light. The compound may cause skin irritation and eye damage; therefore, standard laboratory safety precautions including protective clothing and eye protection are recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: As a masked boronic acid derivative, 4-methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzoic acid is predominantly utilized in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. It serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of meta-substituted biaryl compounds, where the boronate ester group provides enhanced stability and reactivity compared to free boronic acids (Journal of Organic Chemistry). Additionally, the compound participates in the preparation of pharmaceutical intermediates, where its methyl group directs regioselective coupling reactions to form complex aromatic architectures found in GPCR modulators (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters). The carboxylic acid functionality enables further derivatization into amide or ester bonds, expanding its utility in peptide conjugation applications (ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters). In materials science, it functions as monomer for preparing polyboronate hydrogels with tunable degradation rates, where the boronate ester groups hydrolyze under physiological conditions to release bioactive molecules (Biomacromolecules).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review