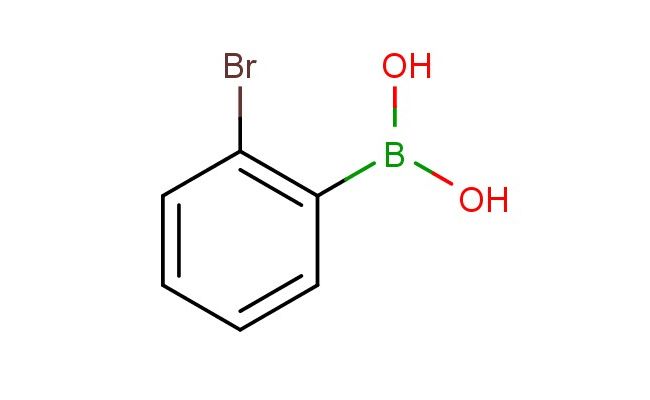
2-bromophenylboronic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 244205-40-1
Catalog No.: 196622
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BBrO2
MW: 200.828
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC1=C(C=CC=C1)B(O)O
Catalog No.: 196622
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BBrO2
MW: 200.828
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC1=C(C=CC=C1)B(O)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
2-bromophenylboronic acid; CAS No.: 244205-40-1; 2-bromophenylboronic acid. PROPERTIES: This brominated boronic acid features molecular formula C6H5BrBO2 with molecular weight 213.91 g/mol. It typically presents as white crystalline solid, exhibiting characteristic reactivity of boronic acid and bromine functionalities. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar solvents like methanol and acetonitrile, while being insoluble in hexanes. Its melting point ranges between 115-119 C, and it exhibits IR absorption bands corresponding to the boronic acid group (~1200-1000 cm??) and aromatic C-H stretches. Thermogravimetric analysis indicates onset decomposition temperature above 200 C under nitrogen. For optimal stability, 2-bromophenylboronic acid should be stored at -20 C in desiccator containing molecular sieves, protected from atmospheric moisture. As with brominated compounds, it may cause severe skin burns and eye damage; therefore, rigorous containment and personal protection measures are essential during manipulation. APPLICATIONS: The bromine substituent of 2-bromophenylboronic acid enables its use as versatile intermediate in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. It participates in Suzuki-Miyaura couplings to form biaryl compounds with diverse electronic properties, as demonstrated in organic synthesis research (Tetrahedron Letters). Additionally, the compound serves as building block in the synthesis of agrochemicals, where the bromine atom provides valuable halogenation site for further functionalization (Pest Management Science). In pharmaceutical development, it functions as key intermediate in the preparation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, where the boronic acid group coordinates with catalytic domain metals while the bromine atom contributes to hydrophobic interactions (European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Furthermore, the compound participates in the synthesis of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications, where its bromine atom enables radiolabeling for PET imaging studies (Bioconjugate Chemistry).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review