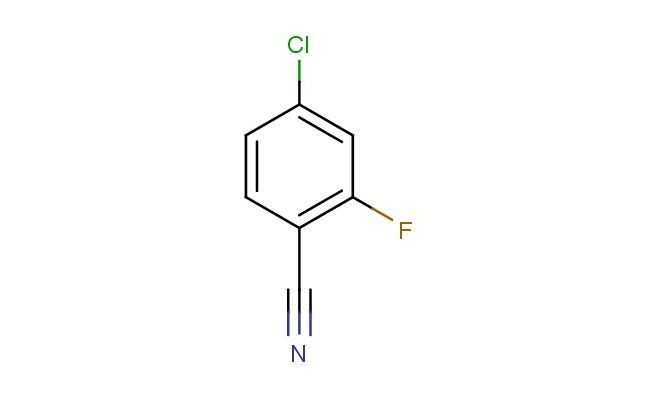
4-chloro-2-fluorobenzonitrile
$300.00
CAS No.: 57381-51-8
Catalog No.: 196636
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H3ClFN
MW: 155.559
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC(=C(C#N)C=C1)F
Catalog No.: 196636
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H3ClFN
MW: 155.559
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC(=C(C#N)C=C1)F
4-chloro-2-fluorobenzonitrile; CAS No.: 57381-51-8; 4-chloro-2-fluorobenzonitrile. PROPERTIES: This chloro-fluoro-substituted nitrile possesses molecular formula C7H4ClFNO with molecular weight 169.57 g/mol. It typically presents as colorless to pale yellow liquid, exhibiting characteristic nitrile reactivity. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar aprotic solvents like DMF and DMSO, while being sparingly soluble in methanol. Its boiling point ranges between 165-170 C at 760 mmHg, and it exhibits IR absorption bands corresponding to the nitrile group (~2220 cm??) and aromatic C-H stretches. Thermogravimetric analysis indicates decomposition onset above 220 C under nitrogen atmosphere. For optimal stability, 4-chloro-2-fluorobenzonitrile should be stored at 2-8 C in tightly sealed amber glass containers, protected from moisture and prolonged light exposure. As with nitrile compounds, it may cause severe skin burns and eye damage; therefore, rigorous containment and personal protection measures are essential during manipulation. APPLICATIONS: As a versatile nitrile derivative, 4-chloro-2-fluorobenzonitrile is particularly effective as building block in pharmaceutical synthesis. It serves as key intermediate in the preparation of beta-blockers, where the nitrile group undergoes hydrolysis to carboxylic acid followed by amidation to form the characteristic amide functionality as demonstrated in medicinal chemistry research (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Additionally, the compound participates in the synthesis of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications, where its nitrile functionality enables conjugation to biomolecules via click chemistry reactions (Bioconjugate Chemistry). In materials science, it functions as monomer for preparing polyacrylonitrile fibers with enhanced thermal stability, where the chloro and fluoro substituents contribute to improved flame retardancy and mechanical properties (Polymer Chemistry). Furthermore, the compound serves as starting material in the development of nitrile-based ligands for transition metal catalysis, where its electron-withdrawing substituents influence catalytic activity and selectivity (Catalysis Science & Technology).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review