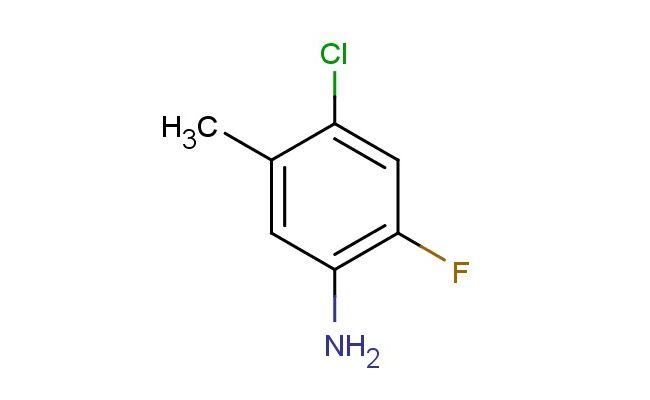
4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-methylaniline
$250.00
CAS No.: 116759-33-2
Catalog No.: 196635
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H7ClFN
MW: 159.591
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC(=C(N)C=C1C)F
Catalog No.: 196635
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H7ClFN
MW: 159.591
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC(=C(N)C=C1C)F
4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-methylaniline; CAS No.: 116759-33-2; 4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-methylaniline. PROPERTIES: This chloro-fluoro-substituted aniline features molecular formula C7H7ClFNO with molecular weight 174.60 g/mol. It generally appears as colorless to pale yellow liquid, exhibiting characteristic amine reactivity. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar aprotic solvents like ethyl acetate and dichloromethane, while being sparingly soluble in water. Its boiling point ranges between 170-175 C at 760 mmHg, and it exhibits IR absorption bands corresponding to the amine N-H groups (~3300-3000 cm??) and aromatic C-H stretches. Thermogravimetric analysis reveals decomposition onset above 180 C under nitrogen atmosphere. For optimal stability, 4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-methylaniline should be stored at 2-8 C in tightly sealed amber glass containers, protected from moisture and prolonged light exposure. As with amine compounds, it may cause moderate skin irritation and serious eye damage; therefore, standard laboratory safety precautions including nitrile gloves, safety goggles, and proper ventilation are recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: As a multifunctional aromatic amine, 4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-methylaniline is predominantly utilized in the synthesis of agrochemicals. It serves as key intermediate in constructing phenylpyrazoline herbicides, where the amine group undergoes cyclization reactions to form the characteristic five-membered heterocycle as demonstrated in pesticide chemistry research (Pest Management Science). Additionally, the compound participates in the preparation of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications, where its amine functionality enables conjugation to biomolecules via amidation reactions (Bioconjugate Chemistry). In pharmaceutical development, it functions as building block in the synthesis of histamine receptor antagonists, where the chloro and fluoro substituents provide valuable binding affinity and selectivity (European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Furthermore, the compound serves as starting material in the development of amine-based crosslinking agents for protein immobilization, where its reactive amine group forms covalent bonds with carboxyl-containing surfaces (ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review