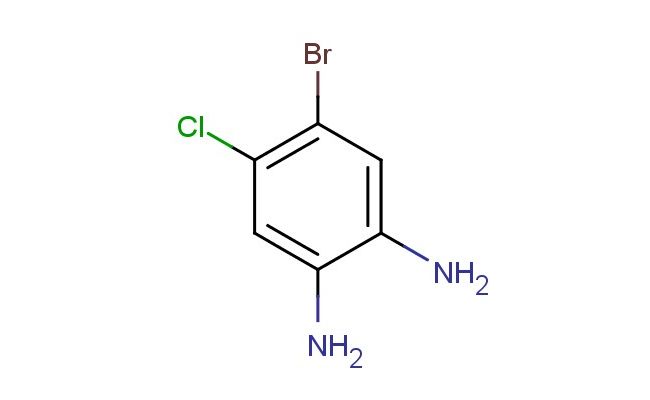
4-bromo-5-chlorobenzene-1,2-diamine
$300.00
CAS No.: 75293-95-7
Catalog No.: 194049
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BrClN2
MW: 221.485
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=C(C(=CC1Cl)N)N
Catalog No.: 194049
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H6BrClN2
MW: 221.485
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=C(C(=CC1Cl)N)N
4-bromo-5-chlorobenzene-1,2-diamine; CAS No.: 75293-95-7; 4-bromo-5-chlorobenzene-1,2-diamine. PROPERTIES: 4-bromo-5-chlorobenzene-1,2-diamine is a crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 231.4 g/mol. It typically exhibits a melting point in the range of 165-168 C and limited water solubility, though it dissolves readily in organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and dimethylformamide. The compound contains reactive functional groups including two amine groups, a bromine substituent, and a chlorine substituent, which contribute to its chemical versatility. For optimal storage, it should be kept in a tightly sealed container at temperatures below 20 C, preferably under inert atmosphere to prevent potential oxidation of the amine functionalities. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective clothing, gloves, and eye/face protection to minimize exposure risk. The compound may cause eye irritation and skin irritation, and in case of accidental ingestion, immediate medical attention is advised. APPLICATIONS: 4-bromo-5-chlorobenzene-1,2-diamine serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, particularly in the development of targeted kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Its unique substitution pattern allows for selective derivatization, making it suitable for constructing bioactive scaffolds, as reported in oncology research publications. In materials science, the compound functions as a building block for certain types of conductive polymers and electroactive materials. The presence of two amine groups provides multiple sites for further functionalization, enabling the creation of complex molecular architectures. Additionally, it is utilized in the preparation of specialty dyes and pigments, particularly those requiring specific optical properties. Through chemical modification of the amine groups, it can be converted into various heterocyclic systems and other functionalized derivatives, expanding its application scope in organic synthesis. The bromine and chlorine substituents provide convenient handles for further functionalization, such as in cross-coupling reactions.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review