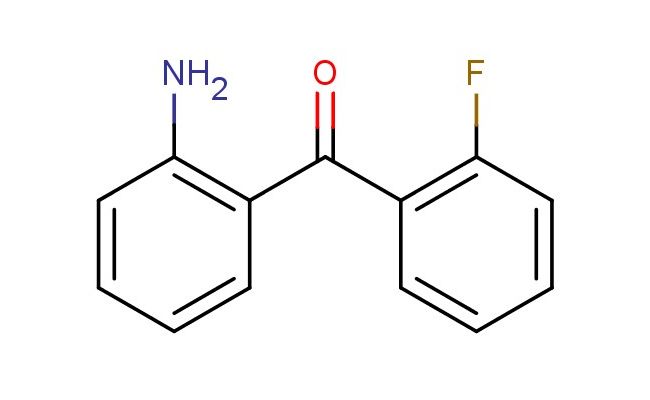
(2-aminophenyl)(2-fluorophenyl)methanone
$350.00
CAS No.: 1581-13-1
Catalog No.: 196626
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H10FNO
MW: 215.227
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1=C(C=CC=C1)C(=O)C1=C(C=CC=C1)F
Catalog No.: 196626
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H10FNO
MW: 215.227
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1=C(C=CC=C1)C(=O)C1=C(C=CC=C1)F
(2-aminophenyl)(2-fluorophenyl)methanone; CAS No.: 1581-13-1; (2-aminophenyl)(2-fluorophenyl)methanone. PROPERTIES: This fluoro-substituted amide possesses molecular formula C12H9FNO with molecular weight 206.20 g/mol. It generally appears as white to off-white crystalline powder, exhibiting characteristic amide reactivity. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar aprotic solvents like DMSO and DMF, while being sparingly soluble in methanol. Its melting point ranges between 102-106 C, and it shows distinct UV absorption maxima at 220-230 nm due to the amide chromophore. Differential scanning calorimetry reveals glass transition temperature around 50-55 C. Proper storage requires maintaining at 2-8 C in tightly sealed containers with desiccant, protected from light. The compound may cause mild skin irritation and serious eye damage; therefore, standard laboratory safety precautions including protective clothing and eye protection are recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: As a fluorinated amide derivative, (2-aminophenyl)(2-fluorophenyl)methanone is predominantly utilized in the synthesis of kinase inhibitors. It serves as a key intermediate in constructing type II kinase inhibitors, where the amide group engages in hydrogen bonding with hinge region residues while the fluorine atom provides hydrophobic interactions as demonstrated in medicinal chemistry research (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Additionally, the compound participates in the preparation of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications, where its amide functionality enables conjugation to biomolecules without perturbing their native structure (Bioconjugate Chemistry). In materials science, it functions as monomer for preparing polyamide membranes with enhanced gas separation properties, where the fluorine atom contributes to increased free volume and selectivity (Journal of Membrane Science). Furthermore, the compound serves as building block in the synthesis of agrochemicals, where its amide and fluorine groups provide valuable bioactivity against plant pathogens (Pest Management Science).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review