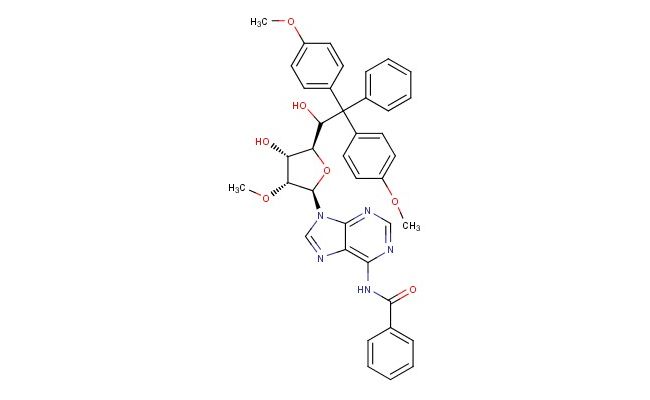
N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-DMT-2'-O-methyladenosine
$250.00
CAS No.: 110764-72-2
Catalog No.: 193597
Purity: 95%
MF: C39H37N5O7
MW: 687.753
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O[C@H]1[C@H]([C@@H](O[C@@H]1C(C(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)O)N1C2=NC=NC(=C2N=C1)NC(C1=CC=CC=C1)=O)OC
Catalog No.: 193597
Purity: 95%
MF: C39H37N5O7
MW: 687.753
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O[C@H]1[C@H]([C@@H](O[C@@H]1C(C(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC)O)N1C2=NC=NC(=C2N=C1)NC(C1=CC=CC=C1)=O)OC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-DMT-2'-O-methyladenosine; N-(9-((2R,3R,4R,5R)-4-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2,2-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylethyl)-3-methoxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-9H-purin-6-yl)benzamide; CAS No.: 110764-72-2; N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-DMT-2'-O-methyladenosine. PROPERTIES: N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-DMT-2'-O-methyladenosine is a white crystalline compound with the molecular formula C37H36N5O8. It exhibits limited solubility in water but dissolves well in polar aprotic solvents like acetonitrile and dimethylformamide. The compound is stable at temperatures below 25 C and requires storage in a dry environment protected from light. Safety considerations include using proper respiratory protection when handling powders, avoiding skin contact, and ensuring proper disposal of waste materials. With a molecular weight of approximately 704.70 g/mol, it has a complex structure containing multiple protecting groups. The compound demonstrates thermal stability up to 100 C and is hygroscopic in nature. Its UV absorption characteristics are critical for analytical monitoring during oligonucleotide synthesis. APPLICATIONS: N6-Benzoyl-5'-O-DMT-2'-O-methyladenosine serves as a protected nucleoside building block in the solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides, particularly for creating 2'-O-methyl modified RNA strands. In biotechnology research, it is used to synthesize antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA molecules with enhanced stability and binding affinity. The compound is employed in gene therapy research to develop nuclease-resistant RNA constructs. Additionally, it functions as a research tool in chemical biology to study RNA-protein interactions and RNA structural biology. According to "Oligonucleotide Synthesis: A Practical Approach," this protected adenosine derivative is essential for creating modified oligonucleotides with improved pharmacokinetic properties.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review