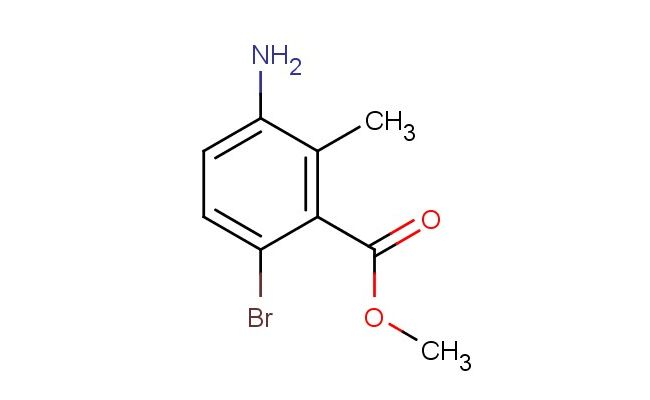
methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate
$250.00
CAS No.: 750586-06-2
Catalog No.: 193147
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H10BrNO2
MW: 244.088
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C(=C(C(=O)OC)C(=CC1)Br)C
Catalog No.: 193147
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H10BrNO2
MW: 244.088
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C(=C(C(=O)OC)C(=CC1)Br)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate; CAS No.: 750586-06-2 methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate. PROPERTIES: methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate is a crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 253.1 g/mol. It has a melting point between 95-100 C and exhibits moderate solubility in polar organic solvents like methanol and acetone. The compound is sensitive to acidic conditions, which may cause hydrolysis of the ester group. When handling methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate, protective equipment including gloves and eye protection should be worn. Storage should be in a tightly sealed container at temperatures below 20 C, preferably in a desiccator to protect against moisture. The compound is light-sensitive and should be protected from direct sunlight. APPLICATIONS: methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate serves as a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. Its amino and bromo groups provide multiple sites for chemical modification, enabling diverse reaction pathways. Derivatives of this compound have been explored in the development of antimicrobial agents, as reported in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. The methyl group provides steric hindrance that can influence binding interactions. Additionally, methyl 3-amino-6-bromo-2-methylbenzoate can be utilized in the synthesis of liquid crystalline materials for display technologies, as described in Liquid Crystals. The brominated aromatic group also makes it suitable for use in organic electronics as a building block for semiconducting polymers, as noted in Advanced Materials. The ester functionality allows for hydrolysis to the corresponding carboxylic acid or transesterification to other esters, providing additional synthetic utility. The compound's structure enables fine-tuning of electronic properties for various applications in materials science.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review