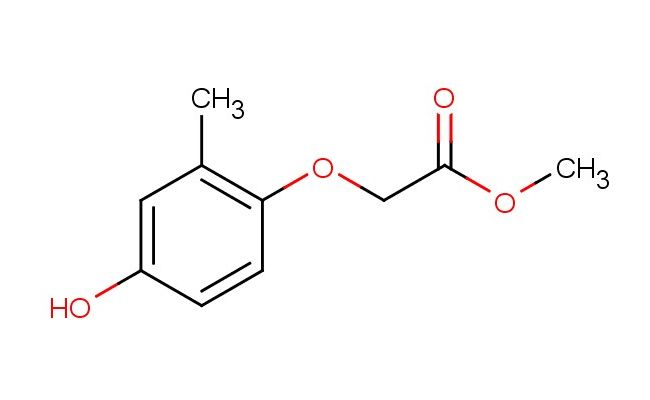
methyl 2-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenoxy)acetate
$250.00
CAS No.: 317319-10-1
Catalog No.: WLZ1204
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H12O4
MW: 196.202
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: OC1=CC(=C(OCC(=O)OC)C=C1)C
Catalog No.: WLZ1204
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H12O4
MW: 196.202
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: OC1=CC(=C(OCC(=O)OC)C=C1)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 317319-10-1; methyl 2-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenoxy)acetate. PROPERTIES: This aryl ether ester combines a methyl ester group with a hydroxylated, methyl-substituted phenoxy moiety, creating a molecule with potential applications in organic synthesis and materials science. The methyl 2-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenoxy)acetate typically presents as a pale yellow crystalline solid with moderate solubility in polar solvents like methanol and ethyl acetate. Its molecular structure includes a phenolic hydroxyl group that can participate in hydrogen bonding interactions, contributing to its crystallization behavior and solubility profile. For optimal stability and to prevent ester hydrolysis, this compound should be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in a tightly sealed container under anhydrous conditions. When handling, chemists should wear appropriate personal protective equipment including nitrile gloves and safety goggles. This compound is sensitive to moisture and may hydrolyze in aqueous environments. In case of skin contact, wash thoroughly with soap and water; if eye contact occurs, rinse immediately and seek medical advice. APPLICATIONS: The methyl 2-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenoxy)acetate serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, particularly those requiring ether and ester functionalities. The phenoxy group provides a platform for further substitution reactions, while the methyl ester offers a protected carboxylic acid functionality. In materials science, this compound functions as a building block for creating liquid crystalline polymers where the rigid aromatic moiety contributes to mesomorphic behavior. Additionally, the molecule finds utility in organic synthesis as a chiral auxiliary for asymmetric transformations, leveraging the steric influence of the methyl-substituted phenoxy group. Researchers utilizing this compound can benefit from its functional group versatility, enabling the development of diverse molecular architectures for applications ranging from drug discovery to advanced materials.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review