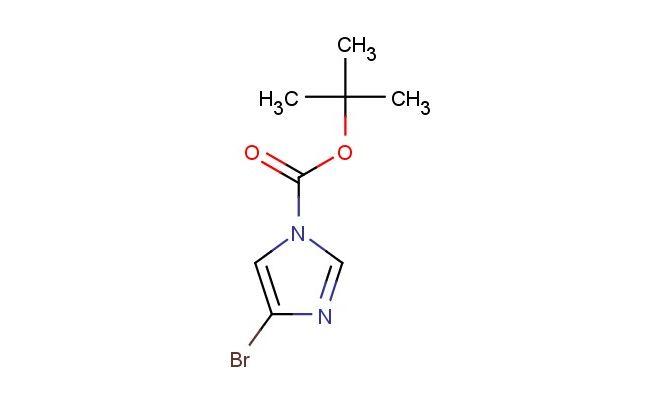
tert-Butyl4-bromo-1H-imidazole-1-carboxylate
$250.00
CAS No.: 1338257-80-9
Catalog No.: WLZ1222
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H11BrN2O2
MW: 247.092
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N1C=NC(=C1)Br
Catalog No.: WLZ1222
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H11BrN2O2
MW: 247.092
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N1C=NC(=C1)Br
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 1338257-80-9; tert-Butyl4-bromo-1H-imidazole-1-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: This protected heterocycle combines a bromine substituent with a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting group on an imidazole ring, creating a molecule with potential applications in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry. The tert-butyl4-bromo-1H-imidazole-1-carboxylate typically appears as a white to off-white crystalline solid with limited aqueous solubility but good solubility in polar aprotic solvents. Its molecular structure includes a Boc group that can be selectively removed under acidic conditions to release the imidazole core. For optimal stability and to prevent premature deprotection, this compound should be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in a tightly sealed container under anhydrous conditions. When handling, chemists should wear appropriate personal protective equipment including nitrile gloves and safety goggles. This compound is sensitive to moisture and may hydrolyze in aqueous environments. In case of skin contact, wash thoroughly with soap and water; if eye contact occurs, rinse immediately and seek medical advice. APPLICATIONS: The tert-butyl4-bromo-1H-imidazole-1-carboxylate serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of imidazole-containing bioactive molecules, particularly in pharmaceutical research. The bromine substituent provides a handle for cross-coupling reactions, enabling the creation of substituted imidazoles with diverse biological activities. In medicinal chemistry, this compound functions as a building block for developing antifungal and antiparasitic agents where the imidazole scaffold contributes to target binding. Additionally, the molecule finds utility in chemical biology studies where its protected amine functionality can be selectively revealed for further conjugation. Researchers utilizing this compound benefit from its functional group compatibility, enabling the development of therapeutic agents targeting various disease pathways including infectious diseases and cancer.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review