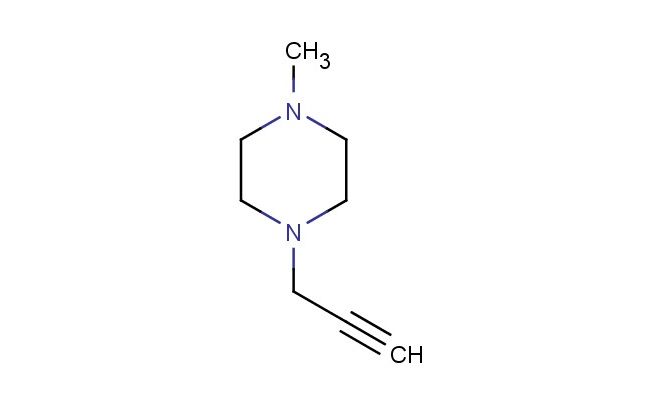
1-methyl-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)piperazine
$250.00
CAS No.: 45813-02-3
Catalog No.: WLZ1220
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H14N2
MW: 138.214
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CN1CCN(CC1)CC#C
Catalog No.: WLZ1220
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H14N2
MW: 138.214
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CN1CCN(CC1)CC#C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 45813-02-3; 1-methyl-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)piperazine. PROPERTIES: This alkylated heterocycle combines a methyl group with a propargyl substituent on a piperazine ring, creating a molecule with potential applications in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry. The 1-methyl-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)piperazine typically presents as a colorless to pale yellow liquid with moderate solubility in common organic solvents. Its molecular structure includes a terminal alkyne moiety that can participate in click chemistry reactions, particularly copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC). For optimal stability and to prevent undesired reactions, this compound should be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in an amber glass bottle under an inert atmosphere. When handling, appropriate safety measures including nitrile gloves and safety goggles are recommended. This compound is sensitive to moisture and may form addition products with protic solvents. In case of accidental ingestion, rinse mouth thoroughly and seek immediate medical attention. APPLICATIONS: The 1-methyl-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)piperazine serves as a valuable building block in bioconjugation chemistry where its alkyne group enables efficient click reactions with azide-tagged biomolecules. The piperazine scaffold provides a flexible platform for creating bioactive molecules with diverse applications. In medicinal chemistry, this compound functions as an intermediate for developing pharmaceuticals targeting the central nervous system, leveraging the piperazine ring's ability to modulate receptor interactions. Additionally, the molecule finds utility in materials science as a monomer for creating polymers with specific electronic and optical properties. Researchers utilizing this compound can benefit from its functional group versatility, enabling the development of diverse molecular architectures for applications ranging from drug discovery to advanced materials.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![3-chloro-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/w/l/wlz1219_1.jpg)