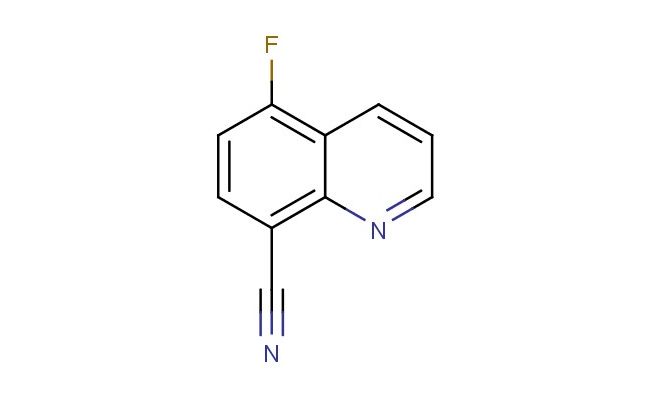
5-fluoroquinoline-8-carbonitrile
$715.00
CAS No.: 1823944-97-3
Catalog No.: 197604
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H5FN2
MW: 172.162
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=C2C=CC=NC2=C(C=C1)C#N
Catalog No.: 197604
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H5FN2
MW: 172.162
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=C2C=CC=NC2=C(C=C1)C#N
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
5-fluoroquinoline-8-carbonitrile; CAS No.: 1823944-97-3;5-fluoroquinoline-8-carbonitrile. PROPERTIES: 5-fluoroquinoline-8-carbonitrile is a heterocyclic aromatic compound featuring a quinoline ring substituted with a fluorine atom at position 5 and a nitrile group at position 8. This white to off-white crystalline solid exhibits typical quinoline characteristics with a molecular weight of 169.13 g/mol. Its physical properties include a melting point ranging between 112-115 C and limited aqueous solubility, demonstrating higher solubility in organic solvents such as dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethylformamide. The compound displays moderate hygroscopic tendencies and should be stored in tightly sealed containers under dry conditions, preferably at temperatures below 25 C. Safety precautions include avoiding inhalation of dust, as the nitrile group poses cyanide-like hazards upon metabolic breakdown, and the fluorine substitution may cause cumulative effects with prolonged exposure. Proper protective equipment including N95 respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and safety goggles is recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: 5-fluoroquinoline-8-carbonitrile serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of specialized agrochemicals and pharmaceutical agents, particularly in developing novel antimicrobial agents where the fluorine substitution enhances bioavailability and the nitrile group provides sites for further functionalization. In medicinal chemistry, this compound has been utilized as a starting material for creating kinase inhibitors, with several derivatives entering preclinical trials for cancer therapy. Its structural framework has also found applications in organic electronics as a component of semiconductor materials, where the electron-deficient quinoline core contributes to charge transport properties. These applications are well-documented in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and Advanced Materials publications focusing on heterocyclic building blocks.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review