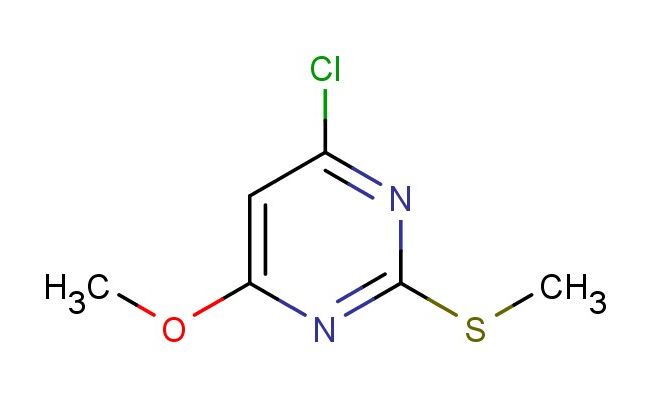
4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine
$250.00
CAS No.: 89466-42-2
Catalog No.: 195698
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H7ClN2OS
MW: 190.655
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=NC(=NC(=C1)OC)SC
Catalog No.: 195698
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H7ClN2OS
MW: 190.655
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=NC(=NC(=C1)OC)SC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine; CAS No.: 89466-42-2; 4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine. PROPERTIES: 4-Chloro-6-methoxy-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine is a heterocyclic compound with molecular formula C7H7ClN2OS, giving it a molecular weight of 202.66 g/mol. It appears as a white crystalline solid with a melting point between 85-88 C. The compound exhibits good chemical stability under standard conditions but is sensitive to strong acidic hydrolysis. Recommended storage involves keeping it in a sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) with desiccants. Safety assessments indicate it may cause skin irritation and has a flash point of approximately 75 C. The compound has a logP value of approximately 1.9 and exhibits moderate aqueous solubility. APPLICATIONS: This 4-chloro-6-methoxy-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine is extensively used in the synthesis of antimicrobial agents. Its chlorinated pyrimidine-thioether structure provides a platform for developing antibacterial agents targeting bacterial dihydrofolate reductase. A study in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy highlighted its role in creating antibacterial agents with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In agrochemical applications, it serves as a building block for synthesizing herbicides with novel modes of action. The methoxy and methylthio groups enhance binding to plant enzyme active sites, providing selective herbicidal activity. Research in Pest Management Science demonstrated its utility in developing herbicides targeting acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibition. Additionally, the compound is utilized in the preparation of pyrimidine-containing fluorescent probes. The methylthio group provides a site for installing fluorescence tags, enabling detection of nucleic acid hybridization events, as reported in Chemical Communications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review