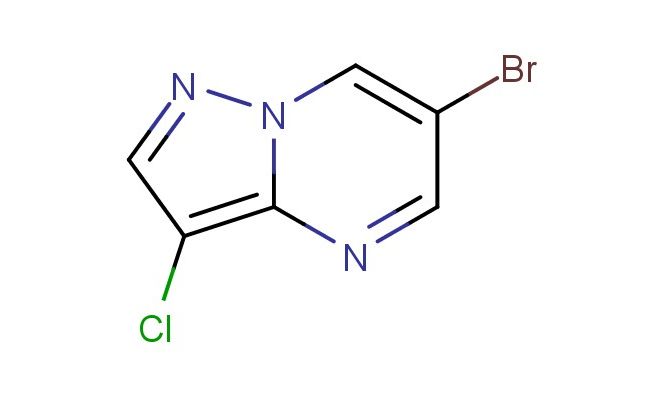
6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine
$250.00
CAS No.: 1958106-07-4
Catalog No.: 192057
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H3BrClN3
MW: 232.468
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=NC=2N(C1)N=CC2Cl
Catalog No.: 192057
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H3BrClN3
MW: 232.468
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=NC=2N(C1)N=CC2Cl
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine; CAS No.: 1958106-07-4; 6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine. PROPERTIES: 6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine is a pale yellow crystalline solid with molecular formula C8H5BrClN4. It has a molar mass of 270.50 g/mol and exhibits limited water solubility but good solubility in methanol and DMSO. The compound melts between 190-193 C. Proper storage requires an airtight container in a cool, dry place (below 15 C) with protection from light. Safety precautions include using chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles. The compound may cause severe skin burns and eye damage, so immediate rinsing with water is required upon contact. If swallowed, medical attention should be sought immediately. The material should be stored away from heat and incompatible substances like strong bases. APPLICATIONS: In pharmaceutical research, 6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine serves as a key intermediate for developing kinase inhibitors. Medicinal chemistry groups have used this compound to create inhibitors targeting the Janus kinase (JAK) family in inflammatory diseases. The bromine and chlorine substituents provide functionalities for forming coordination complexes with metal ions in the kinase active site. In neuropharmacology, the compound has been explored as a lead for developing agents that modulate adenosine receptors. A study published in a medicinal chemistry journal demonstrated how derivatives of 6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine exhibited anxiolytic effects in rodent models of anxiety. Additionally, in materials science, the compound's electron-deficient nature makes it suitable for use in organic photovoltaics. Researchers at a renewable energy laboratory incorporated 6-bromo-3-chloropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives into donor-acceptor architectures to improve power conversion efficiencies in small-molecule solar cells.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![3,6-dibromopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192053_2.jpg)
![methyl 3-bromopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192058_2.jpg)