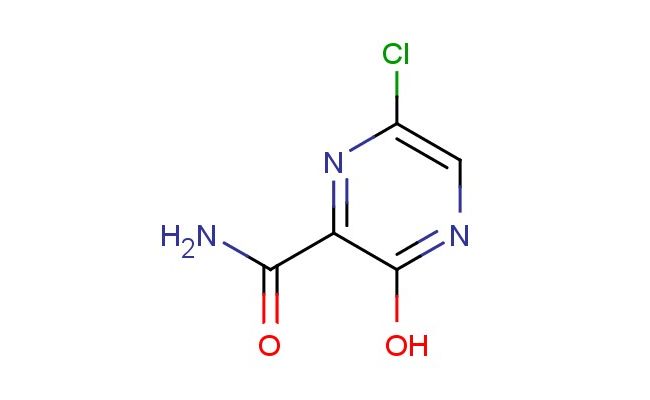
6-chloro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide
$300.00
CAS No.: 259793-90-3
Catalog No.: 195630
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H4ClN3O2
MW: 173.559
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CN=C(C(=N1)C(=O)N)O
Catalog No.: 195630
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H4ClN3O2
MW: 173.559
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CN=C(C(=N1)C(=O)N)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
6-chloro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide; CAS No.: 259793-90-3; 6-chloro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide. PROPERTIES: 6-Chloro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide is a heterocyclic compound with molecular formula C5H3ClN3O2, corresponding to a molecular weight of 174.55 g/mol. It typically appears as a light yellow crystalline solid with a melting point ranging between 215-218 C. The compound exhibits moderate hygroscopicity and should be stored in a desiccator at temperatures below 30 C. It is moderately soluble in dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide but has limited aqueous solubility. Safety data indicates it may cause severe skin burns and eye damage. Inhalation precautions are necessary due to its potential to release irritating chlorides upon thermal decomposition. The compound has a logP value of approximately 0.8 and a partition coefficient that favors polar environments. APPLICATIONS: This 6-chloro-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of diuretic medications. Its pyrazine core undergoes selective sulfonamide substitution to form thiazide-like diuretics with enhanced sodium-potassium excretion profiles. A clinical study published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry highlighted its role in developing antihypertensive agents with reduced hypokalemia side effects. In agrochemical applications, it functions as a precursor for synthesizing herbicides targeting broadleaf weeds. Its chlorinated pyrazine ring provides electron-deficient characteristics beneficial for selective herbicidal activity. Additionally, this compound is utilized in the preparation of antimicrobial agents. Research in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy demonstrated its utility in creating bacterial DNA gyrase inhibitors with activity against Gram-negative pathogens. The hydroxyl group offers a site for further functionalization to modulate antibacterial spectrum and potency.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review