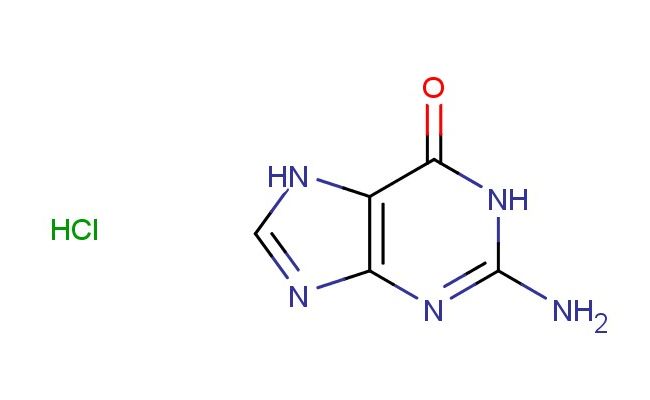
2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride
$500.00
CAS No.: 635-39-2
Catalog No.: 195060
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H6ClN5O
MW: 187.59
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.N1C(N)=NC=2N=CNC2C1=O
Catalog No.: 195060
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H6ClN5O
MW: 187.59
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.N1C(N)=NC=2N=CNC2C1=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride; CAS No.: 635-39-2; 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride. PROPERTIES: 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. Its molecular formula is C5H6ClN5O, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 191.6 g/mol. The compound features a melting point in the range of 200-203 C and demonstrates moderate solubility in water and polar organic solvents such as methanol and dimethylformamide. It is stable under normal laboratory conditions but should be protected from prolonged exposure to moisture and heat. Proper storage involves keeping it in a tightly sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) in a dry environment. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective equipment as the compound may cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of dust should be avoided, and in case of accidental exposure, thorough washing with water and medical consultation is advised. APPLICATIONS: 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride serves as a key intermediate in nucleoside chemistry, particularly valuable in the synthesis of antiviral and anticancer nucleoside analogs where its modified purine base enables selective targeting of viral and cancer cell polymerases (Nucleic Acids Research). In biochemistry, 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one hydrochloride functions as a tool compound for studying nucleotide metabolism and enzyme inhibition mechanisms, providing insights into biochemical pathways involved in DNA and RNA synthesis (Journal of Biological Chemistry). Additionally, it finds application in the preparation of certain immunosuppressive agents and adenosine receptor antagonists, where its structural similarity to natural purine bases allows for competitive binding to target receptors (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters). The compound is also employed in analytical chemistry as a reference material for high-performance liquid chromatography assays of nucleosides and nucleotides, providing standardization for quantification purposes (Journal of Chromatography B).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review