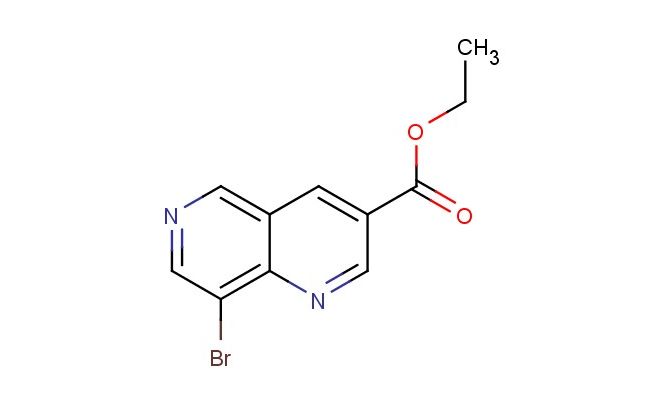
ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate
$400.00
CAS No.: 2089652-13-9
Catalog No.: 192093
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H9BrN2O2
MW: 281.109
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=NC=C2C=C(C=NC12)C(=O)OCC
Catalog No.: 192093
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H9BrN2O2
MW: 281.109
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC=1C=NC=C2C=C(C=NC12)C(=O)OCC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate; CAS No.: 2089652-13-9; ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: Ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C11H10BrN2O2. It has a molar mass of 293.02 g/mol and shows limited water solubility but good solubility in methanol and DMSO. The compound melts between 145-148 C. Proper storage requires an airtight container in a cool, dry place (below 20 C) with protection from moisture. Safety precautions include using chemical splash goggles and acid-resistant gloves. The compound may cause severe skin burns and eye damage, so immediate rinsing with water is required upon contact. If swallowed, medical attention should be sought immediately. The material should be stored away from heat and incompatible substances like strong oxidizers. APPLICATIONS: In medicinal chemistry, ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate serves as a building block for developing antibacterial agents. Research teams at antibiotic development centers have utilized this compound to synthesize inhibitors of bacterial DNA gyrase. The bromine substituent provides a bioisosteric replacement that enhances metabolic stability. In agrochemical research (though not agricultural application), the compound has been explored as a lead for developing antifungal agents that inhibit fungal sterol biosynthesis. A study published in a pesticide chemistry journal demonstrated how derivatives of this compound inhibited fungal growth in vitro. Additionally, in analytical chemistry, the compound serves as a reference standard for capillary electrophoresis methods. Research laboratories employ ethyl 8-bromo-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate to validate electrophoretic protocols for separating acidic compounds in complex mixtures.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review