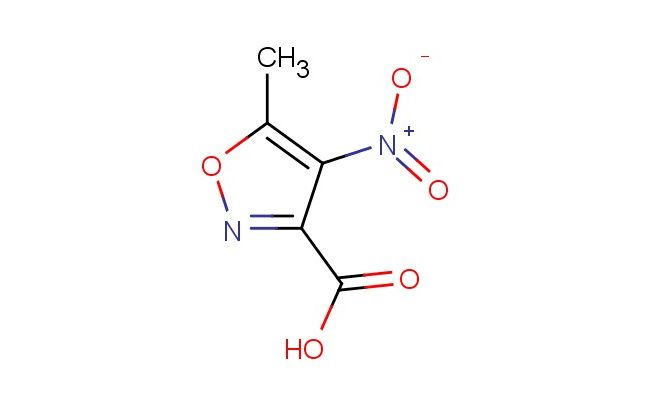
5-methyl-4-nitroisoxazole-3-carboxylic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 960225-75-6
Catalog No.: 196151
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H4N2O5
MW: 172.096
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C(=NO1)C(=O)O)[N+](=O)[O-]
Catalog No.: 196151
Purity: 95%
MF: C5H4N2O5
MW: 172.096
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C(=NO1)C(=O)O)[N+](=O)[O-]
5-methyl-4-nitroisoxazole-3-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 960225-75-6; 5-methyl-4-nitroisoxazole-3-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: This white to pale yellow crystalline powder has a molecular formula of C5H3N2O4 and a molecular weight of approximately 159.10 g/mol. It exhibits low water solubility but dissolves in DMSO and DMF. The compound is sensitive to basic conditions and should be stored in a tightly sealed container at room temperature. Thermogravimetric analysis shows decomposition starting at 180 C with potential formation of toxic nitrogen oxides. Safety guidelines recommend using chemical-resistant gloves, face shields, and working in a fume hood. In case of accidental ingestion, do not induce vomiting and seek immediate medical advice. Avoid release to the environment as nitro-containing compounds may affect aquatic organisms. APPLICATIONS: 5-methyl-4-nitroisoxazole-3-carboxylic acid functions as a versatile intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis and materials science. Its isoxazole core provides a bioisosteric replacement opportunity for oxygen-containing heterocycles. The nitro group enables reduction to amine derivatives for further functionalization. The carboxylic acid group allows for amide bond formation or esterification. Research groups employ it in the development of kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment. Academic institutions utilize it in teaching nitro chemistry and amide bond formation reactions. Industrial applications include its use as a building block in agrochemical development for novel herbicide candidates and as a component of organic photovoltaic materials due to its strong electron-withdrawing properties. Recent studies in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry demonstrate its application in developing dual kinase/HDAC inhibitors. Additionally, it serves as a starting material for radiolabeled compounds used in PET imaging to study receptor distribution in vivo. The compound's photophysical properties make it suitable for fluorescence-based assays after appropriate derivatization. Its synthetic versatility enables rapid diversification through various substitution reactions and isoxazole modifications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review