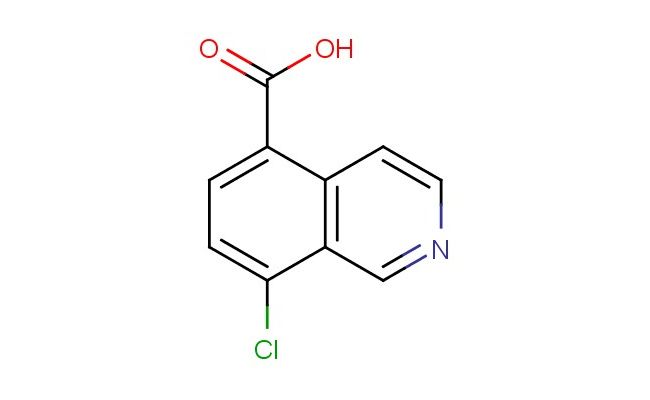
8-chloroisoquinoline-5-carboxylic acid
$600.00
CAS No.: 945470-53-1
Catalog No.: 191956
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6ClNO2
MW: 207.616
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC=C(C=2C=CN=CC12)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 191956
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6ClNO2
MW: 207.616
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CC=C(C=2C=CN=CC12)C(=O)O
8-chloroisoquinoline-5-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 945470-53-1; 8-chloroisoquinoline-5-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 8-chloroisoquinoline-5-carboxylic acid (CAS No.: 945470-53-1) presents as a white crystalline powder with a melting point between 210-213 C. The compound features a chlorine atom at position 8 and a carboxylic acid at position 5 of the isoquinoline ring system. Its carboxylic acid group demonstrates typical acidity with a pKa around 3.5, while the chlorine substituent imparts moderate electron-withdrawing effects. Solubility characteristics reveal good dissolvability in polar solvents like methanol and DMF, with limited water solubility due to the hydrophobic aromatic system. The substance is moisture-sensitive and prone to hydrolysis under basic conditions, necessitating storage in a tightly sealed container under nitrogen atmosphere at controlled room temperature (15-25 C). Safety precautions include using P295 respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and eye protection due to potential skin irritation and eye damage. The compound has a moderate vapor pressure and forms flammable mixtures with air above 60 C. APPLICATIONS: 8-chloroisoquinoline-5-carboxylic acid serves as a valuable intermediate in developing antibacterial agents with activity against Gram-positive pathogens as documented in antimicrobial research. Its chlorinated isoquinoline core enables the synthesis of antiviral agents targeting RNA viruses as reported in virology literature. Additionally, 945470-53-1 contributes to the development of fluorescent probes for detecting specific protein targets in cellular environments, with several studies highlighting its utility in creating pH-sensitive indicators for monitoring endocytic processes during drug delivery. The compound also functions as a building block for materials science applications in developing electron-deficient monomers for conjugated polymers used in organic electronics.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review