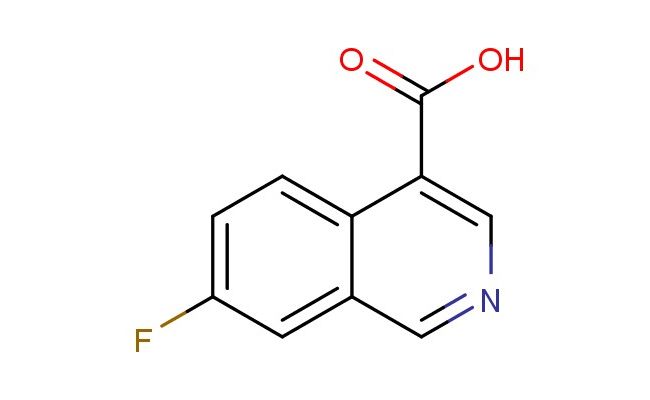
7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid
$600.00
CAS No.: 1841081-40-0
Catalog No.: 191987
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6FNO2
MW: 191.161
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=CC=C2C(=CN=CC2=C1)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 191987
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6FNO2
MW: 191.161
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=CC=C2C(=CN=CC2=C1)C(=O)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 1841081-40-0;7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid is a halogenated heterocyclic carboxylic acid with molecular formula C10H5FNO2. This crystalline powder typically appears off-white and has a melting point ranging between 220-225 C. The molecule contains an isoquinoline core with a fluorine atom at position 7 and a carboxylic acid group at position 4. The 7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid exhibits acidic character with a pKa value around 3.0 for the carboxylic acid group. It demonstrates moderate solubility in water and good solubility in polar organic solvents like methanol. Proper storage requires a tightly sealed container in a cool, dark environment below 25 C to prevent moisture-induced degradation. Safety precautions include using N95 respiratory protection and chemical-resistant gloves, as the compound may cause respiratory irritation and skin corrosion. According to GHS classification, it carries H314 and H335 hazard statements for causing severe skin burns and respiratory tract irritation. APPLICATIONS: The 7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid structure functions as a versatile intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis, particularly valuable for creating isoquinoline-based non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as reported in medicinal chemistry journals. The fluorine substituent provides a site for further functionalization via nucleophilic substitution reactions. Additionally, 7-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid derivatives have been investigated for their potential as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry matrices, as described in analytical chemistry research. The compound's ability to form stable complexes with organic molecules has also made it useful in developing chemical probes for biomolecular interaction studies, as documented in bioanalytical chemistry publications focusing on protein-ligand binding assays.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review