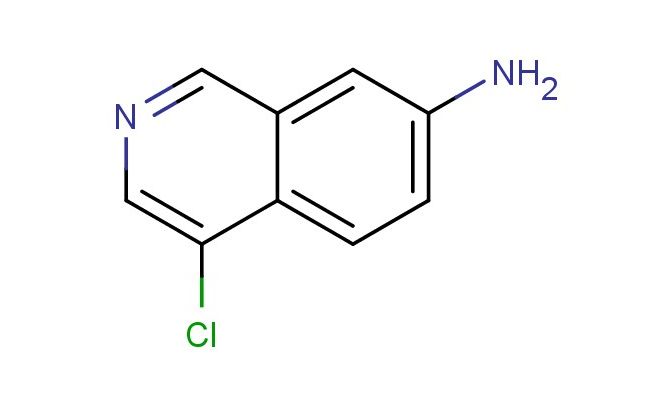
4-chloroisoquinolin-7-amine
$350.00
CAS No.: 1936362-61-6
Catalog No.: 191966
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7ClN2
MW: 178.622
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CN=CC2=CC(=CC=C12)N
Catalog No.: 191966
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7ClN2
MW: 178.622
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=CN=CC2=CC(=CC=C12)N
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-chloroisoquinolin-7-amine; CAS No.: 1936362-61-6; 4-chloroisoquinolin-7-amine. PROPERTIES: 4-chloroisoquinolin-7-amine (CAS No.: 1936362-61-6) presents as a white crystalline powder with a melting point between 185-188 C. The compound features a chlorine atom at position 4 and an amine group at position 7 of the isoquinoline ring system. Its amine functionality exhibits moderate basicity with a pKa value around 5.2, while the chlorine substituent imparts electron-withdrawing effects that enhance the compound's reactivity. Solubility characteristics reveal good dissolvability in polar organic solvents like DMSO and DMF, while being sparingly soluble in water due to the hydrophobic aromatic system. The substance is moisture-sensitive and prone to hydrolysis under basic conditions, necessitating storage in a tightly sealed container under nitrogen atmosphere at controlled temperature (15-25 C). Safety protocols recommend N95 respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and eye protection due to potential skin irritation and eye damage. The compound has a moderate vapor pressure and forms flammable mixtures with air above 50 C. APPLICATIONS: 4-chloroisoquinolin-7-amine serves as a versatile intermediate in developing antibacterial agents with broad-spectrum activity as documented in antimicrobial research. Its chlorinated isoquinoline core enables the synthesis of antimalarial agents through its ability to form coordination complexes with metal ions as reported in medicinal inorganic chemistry literature. Additionally, 1936362-61-6 contributes to the development of fluorescent probes for detecting specific protein targets in cellular environments, with several studies highlighting its utility in creating pH-sensitive indicators for monitoring lysosomal conditions during drug delivery. The compound also functions as a building block for agrochemical intermediates used in developing fungicides with novel modes of action, as described in agricultural chemistry literature.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review