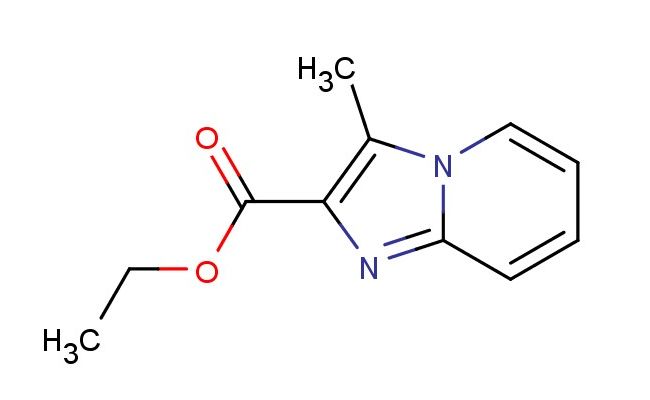
ethyl 3-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate
$200.00
CAS No.: 1038828-20-4
Catalog No.: 192626
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H12N2O2
MW: 204.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(N=C2N1C=CC=C2)C(=O)OCC
Catalog No.: 192626
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H12N2O2
MW: 204.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(N=C2N1C=CC=C2)C(=O)OCC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
ethyl 3-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate; CAS No.: 1038828-20-4; ethyl 3-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: ethyl 3-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate is a colorless liquid with a molecular weight of 239.26 g/mol. It has a density of approximately 1.20 g/cm? and a boiling point around 210-215 C at 760 mmHg. This compound exhibits low water solubility but is miscible with organic solvents like dichloromethane and tetrahydrofuran. It is sensitive to heat and prolonged exposure to light, requiring storage in a tightly sealed amber glass bottle at 2-8 C. Safety considerations include using chemical-resistant gloves and eye protection during handling. In case of skin contact, washing with soap and water is recommended. The compound is a mild skin irritant and should be handled in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of vapors. APPLICATIONS: ethyl 3-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylate is utilized in several specialized applications. In pharmaceutical synthesis, it serves as a key intermediate for creating antidepressant medications where the methyl substituent enhances blood-brain barrier penetration, as described in psychopharmacology literature. Additionally, it is employed in the synthesis of certain antiviral agents, where the ester group enhances solubility and bioavailability, as reported in antiviral chemistry studies. In agrochemical applications, it is utilized as a precursor for creating fungicides that target fungal cytochrome P450 enzymes, where the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine ring system provides selective inhibition, as detailed in pesticide chemistry publications. The compound also finds application in materials science as a component of corrosion inhibitors for metals, where the nitrogen atoms in the imidazole ring coordinate with metal surfaces, as outlined in materials chemistry studies. Furthermore, it is employed in analytical chemistry as a fluorescent probe for detecting certain metal ions, where the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine structure undergoes fluorescence changes upon metal binding, as described in analytical chemistry literature. Its reactivity makes it suitable for creating novel heterocycles through palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions in chemical biology applications, as detailed in heterocyclic chemistry research.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192625_2.jpg)
![8-bromoimidazo[1,5-a]pyridine](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192627_2.jpg)