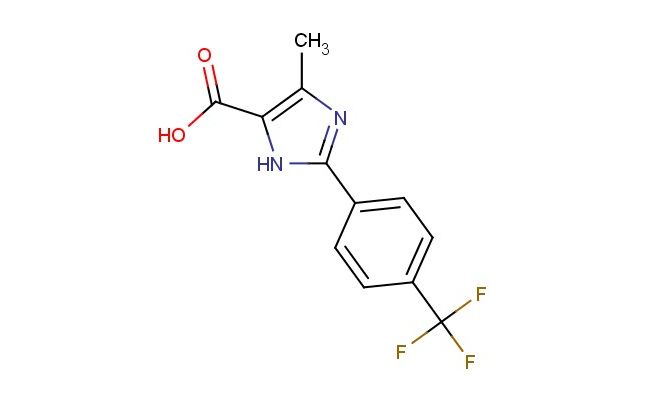
4-methyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 1260810-09-0
Catalog No.: 197809
Purity: 95%
MF: C12H9F3N2O2
MW: 270.21
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC=1N=C(NC1C(=O)O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(F)(F)F
Catalog No.: 197809
Purity: 95%
MF: C12H9F3N2O2
MW: 270.21
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC=1N=C(NC1C(=O)O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(F)(F)F
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-methyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 1260810-09-0;4-methyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 4-methyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid is a trifluoromethylated imidazole carboxylic acid with a molecular weight of 269.21 g/mol. This white crystalline solid has a melting point between 195-198 C. The molecule features an imidazole ring substituted with a methyl group at position 4 and a 4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl group at position 2, with a carboxylic acid group at position 5. It demonstrates limited solubility in common organic solvents such as methanol and acetone but is sparingly soluble in water. Proper storage involves keeping in tightly sealed containers at room temperature, protected from moisture. Safety considerations include the trifluoromethyl group's potential to release toxic fumes when heated and the carboxylic acid's corrosive nature. Proper protective measures should be taken during handling. APPLICATIONS: This compound primarily serves as a building block in the synthesis of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals, where the trifluoromethyl-substituted imidazole structure provides essential binding affinity to target enzymes. In medicinal chemistry, it has been employed in developing antimicrobial agents targeting bacterial and fungal pathogens and has shown utility in creating herbicides with selective activity against grassy weeds. The imidazole-carboxylic acid structure has also been explored in materials science for developing fluorescent probes, leveraging the electron-deficient trifluoromethyl group to tune optical properties. These applications are documented in publications from the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and Dyes and Pigments.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review