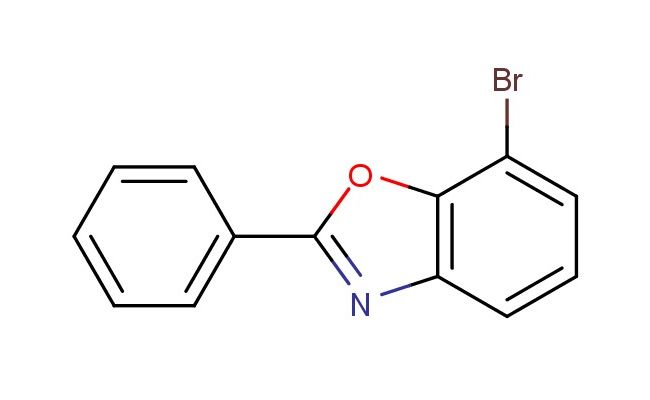
7-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole
$300.00
CAS No.: 1268137-13-8
Catalog No.: TQP2235
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H8BrNO
MW: 274.117
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC1=CC=CC=2N=C(OC21)C2=CC=CC=C2
Catalog No.: TQP2235
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H8BrNO
MW: 274.117
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: BrC1=CC=CC=2N=C(OC21)C2=CC=CC=C2
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 1268137-13-8; 7-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole. PROPERTIES: 7-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole appears as off-white crystalline powders with a slight sulfurous odor. Its molecular formula is C13H8BrNO, with a molecular weight of 275.12 g/mol. The compound demonstrates minimal solubility in water but dissolves in hot methanol and ethyl acetate. Storage at 2-8 degree Celsius in desiccators with appropriate drying agents is necessary to prevent moisture-induced degradation. When handling, avoid skin contact as it may cause allergic dermatitis in sensitive individuals. The substance is stable under nitrogen atmosphere but oxidizes slowly in air, leading to discoloration over time. It has a flash point above 70 C, requiring careful heating protocols during synthetic operations. APPLICATIONS: 7-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole serves as a valuable precursor in the synthesis of biaryl compounds through transition metal-catalyzed couplings. The bromine substituent at the 7-position provides an optimal position for Suzuki-Miyaura reactions, enabling the introduction of diverse aryl groups. In pharmaceutical development, this compound is used to create antidepressant agents where the phenyl substitution modulates receptor binding affinity. The oxazole ring system contributes to metabolic stability, prolonging the duration of action for resulting pharmaceuticals. In materials science, the compound is incorporated into polymeric systems to enhance mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Researchers in sensory chemistry utilize this compound to develop odorants with specific detection profiles, exploiting the oxazole ring's contribution to olfactory perception. Additionally, the compound functions as a ligand in asymmetric catalysis, directing enantioselective outcomes in epoxidation and hydrogenation reactions. The strategic positioning of substituents allows for fine-tuning of electronic properties, making derivatives suitable for optoelectronic applications where charge balance is critical.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![5-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/t/q/tqp2234_1.jpg)
![4-bromo-2-phenylbenzo[d]oxazole](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/t/q/tqp2236_1.jpg)