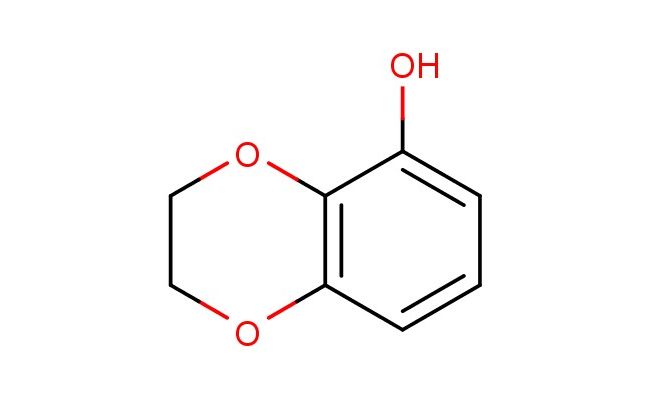
2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-5-ol
$300.00
CAS No.: 10288-36-5
Catalog No.: 196139
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H8O3
MW: 152.149
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O1C2=C(OCC1)C(=CC=C2)O
Catalog No.: 196139
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H8O3
MW: 152.149
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O1C2=C(OCC1)C(=CC=C2)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-5-ol; CAS No.: 10288-36-5; 2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-5-ol. PROPERTIES: This white to off-white crystalline powder has a molecular formula of C8H8O3 and a molecular weight of approximately 156.15 g/mol. It exhibits moderate solubility in water and common polar solvents. The compound is sensitive to acidic conditions and should be stored in a tightly sealed container at room temperature. Thermogravimetric analysis shows decomposition starting at 200 C. Safety guidelines recommend using chemical-resistant gloves, splash goggles, and working in a well-ventilated area. In case of accidental ingestion, rinse mouth and seek immediate medical advice. Avoid release to the environment as it may be harmful to aquatic organisms. APPLICATIONS: 2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-5-ol serves as a valuable intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis, particularly in the development of kinase inhibitors and receptor modulators. Its dioxane core provides conformational constraints useful in controlling bioactive conformations. The hydroxyl group at position 5 enables further functionalization through ether formation or esterification. Research groups employ it in the development of estrogen receptor modulators for breast cancer treatment. Academic institutions utilize it in teaching heterocyclic chemistry and glycosylation reactions. Industrial applications include its use as a building block in agrochemical development for novel fungicide candidates targeting enzyme inhibition. Recent publications in Organic Process Research & Development highlight its role in developing more efficient synthetic routes to glycoside mimetics. Additionally, it finds utility in materials science as a component of pH-responsive polymeric materials. The compound's ability to form hydrogen bonds makes it suitable for crystallographic studies of protein-ligand complexes. Its synthetic versatility enables rapid diversification through various hydroxyl group reactions and dioxane ring modifications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![2-bromo-1-(2,2-dimethyl-4H-benzo[d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl)ethanone](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/5/150915_1.jpg)
![2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine-5-carboxylic acid](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/196140_2.jpg)