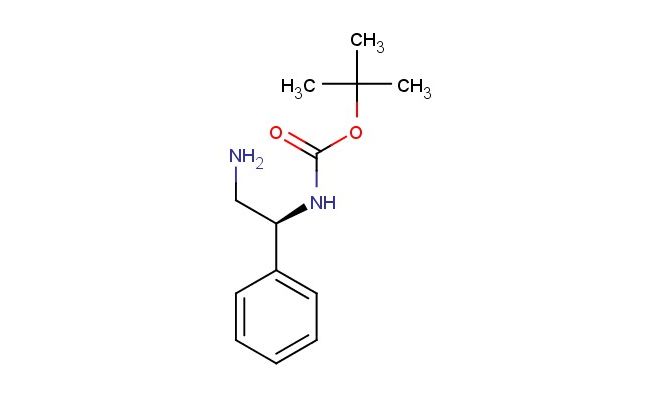
(S)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate
$400.00
CAS No.: 137102-30-8
Catalog No.: TQP2157
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H20N2O2
MW: 236.315
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC[C@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O
Catalog No.: TQP2157
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H20N2O2
MW: 236.315
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC[C@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 137102-30-8; (S)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate. PROPERTIES: (S)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate presents as a white to off-white crystalline powder with a melting point ranging from 128-132 C. Its molecular formula is C11H15N2O2, corresponding to a molecular weight of 207.25 g/mol. The compound exhibits limited solubility in aqueous solutions but dissolves well in common organic solvents like methanol and THF. Proper storage requires maintaining temperatures between 2-8 degree Celsius in amber glass containers to protect against light-induced degradation. When handling, care should be taken to prevent eye contact as it may cause severe eye irritation. The substance is classified as a mild irritant and should be managed in well-ventilated areas. It is stable for extended periods when stored under recommended conditions but may hydrolyze in the presence of moisture over time. APPLICATIONS: (S)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate is predominantly utilized as a chiral intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry. Its enantiomeric purity makes it suitable for synthesizing optically active drugs where spatial configuration determines therapeutic efficacy. The compound serves as a key precursor in the preparation of ACE inhibitors and other cardiovascular agents where the (S)-configuration confers specific bioactivity. In academic research, this carbamate derivative is employed in protein synthesis studies, enabling the incorporation of non-natural amino acids with defined stereochemistry. Its Boc protection group allows for orthogonal protection strategies in solid-phase peptide synthesis, facilitating the assembly of complex peptide architectures. Additionally, the compound functions as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis, directing stereoselective outcomes in various carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The phenylalanine-derived structure provides valuable scaffold for developing enzyme inhibitors with improved kinetic properties.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review