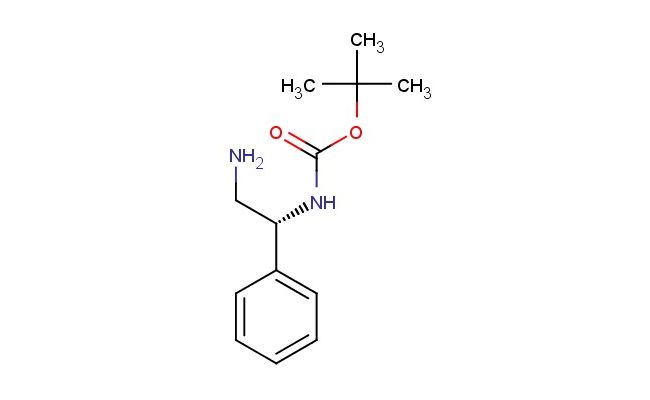
(R)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate
$465.00
CAS No.: 137102-65-9
Catalog No.: TQP2155
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H20N2O2
MW: 236.315
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC[C@@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O
Catalog No.: TQP2155
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H20N2O2
MW: 236.315
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC[C@@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 137102-65-9; (R)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate. PROPERTIES: (R)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate is a white powder with a faint aromatic odor. The compound has a molecular formula of C11H15N2O2 and a molecular weight of 207.25 g/mol. It demonstrates moderate solubility in polar organic solvents while being practically insoluble in water. This chiral compound must be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in a desiccator to maintain stability and prevent degradation. Safety precautions include using a fume hood during handling to avoid inhalation of dust particles, which may cause respiratory irritation. The substance is stable under inert atmosphere but degrades upon prolonged exposure to light and moisture. Glove protection is essential as it may cause skin sensitization in susceptible individuals. APPLICATIONS: (R)-tert-butyl (2-amino-1-phenylethyl)carbamate functions as a crucial chiral building block in the synthesis of optically active pharmaceuticals. Its unique structural features make it particularly useful in the preparation of enantiomerically pure beta-amino acids and related compounds. In peptide synthesis, this carbamate derivative enables the creation of stereochemically defined peptide bonds, enhancing the biological activity of resulting peptide analogs. The compound serves as a starting material for synthesizing various CNS-active drugs where the phenylalanine-derived structure confers specific receptor binding properties. Additionally, its Boc protection allows for controlled deprotection strategies in sequential synthetic pathways, making it indispensable in multi-step total syntheses of complex natural products. Researchers in asymmetric catalysis employ this compound as a ligand precursor, facilitating enantioselective transformations with high stereoselectivity in catalytic processes.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review