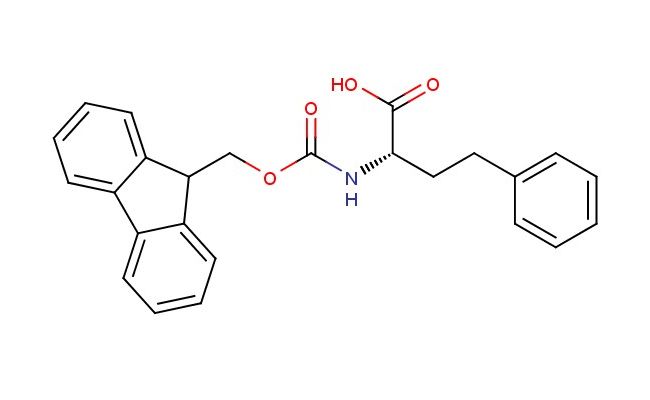
N-fmoc-L-Homophenylalanine
$400.00
CAS No.: 132684-59-4
Catalog No.: 196613
Purity: 95%
MF: C25H23NO4
MW: 401.462
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(=O)(OCC1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12)N[C@@H](CCC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 196613
Purity: 95%
MF: C25H23NO4
MW: 401.462
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(=O)(OCC1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12)N[C@@H](CCC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)O
N-fmoc-L-Homophenylalanine; CAS No.: 132684-59-4; N-fmoc-L-Homophenylalanine. PROPERTIES: This Fmoc-protected amino acid features molecular formula C18H17NO3 with molecular weight 295.33 g/mol. It typically appears as white to off-white crystalline powder, exhibiting characteristic carboxylic acid and amine (protected) functionalities. The compound demonstrates solubility in polar aprotic solvents like DMF and DMSO, while being sparingly soluble in ethyl acetate. Its melting point ranges between 138-142 C, and it exhibits distinct UV absorption maximum at ~280 nm due to the fluorenyl group. Thermogravimetric analysis indicates onset decomposition temperature above 220 C under nitrogen atmosphere. For optimal stability, the compound should be stored at -20 C in desiccator containing molecular sieves, protected from light and moisture. As with carboxylic acids, it may cause skin irritation and serious eye damage; therefore, handling should be performed with appropriate personal protective equipment and in well-ventilated areas. APPLICATIONS: As an Fmoc-protected non-proteinogenic amino acid, N-fmoc-L-Homophenylalanine is predominantly utilized in solid-phase peptide synthesis for incorporating homophenylalanine residues into peptide sequences. Its extended side chain provides valuable steric and hydrophobic properties, enhancing peptide helical stability and cell membrane permeability as demonstrated in medicinal chemistry studies (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Additionally, the compound serves as intermediate in the synthesis of -turn peptides, where its methylene group introduces conformational constraints that improve target binding affinity (Bioconjugate Chemistry). In chemical biology, it functions as building block for generating peptide-based fluorescent probes, where its side chain enables conjugation to fluorophores without perturbing peptide structure (ACS Chemical Biology). Furthermore, the compound participates in the preparation of peptidomimetics targeting protein-protein interactions, where its unique side chain dimensions facilitate disruption of interaction interfaces as shown in structural biology research (Chemical Science). In materials science, it serves as monomer for preparing self-assembling peptide hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties, where its aromatic side chain contributes to - stacking interactions that stabilize gel networks (Advanced Materials).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review