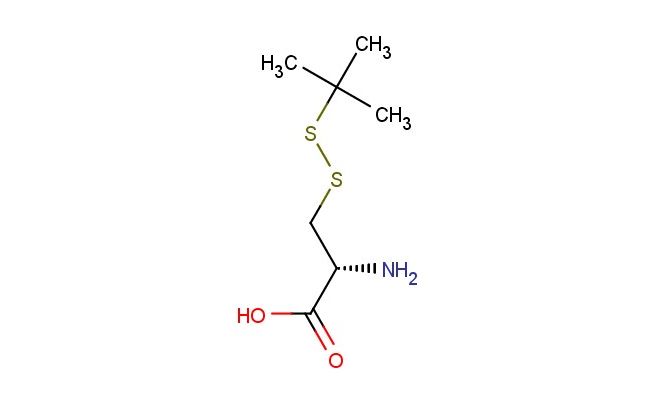
S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine
$300.00
CAS No.: 30044-51-0
Catalog No.: 195053
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H15NO2S2
MW: 209.336
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)SSC[C@H](N)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 195053
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H15NO2S2
MW: 209.336
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)SSC[C@H](N)C(=O)O
S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine; CAS No.: 30044-51-0; S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine. PROPERTIES: S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder with a slight sulfur odor. Its molecular formula is C11H18N2O2S2, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 270.41 g/mol. The compound exhibits a melting point in the range of 150-153 C and demonstrates moderate solubility in water, with increased solubility in polar organic solvents such as methanol and dimethylformamide. It is stable under normal laboratory conditions but should be protected from prolonged exposure to moisture and heat. Proper storage involves keeping it in a tightly sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) in a dry environment. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective equipment as the compound may cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of dust should be avoided, and in case of accidental exposure, thorough washing with water and medical consultation is advised. APPLICATIONS: S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine serves as a specialized intermediate in biochemical research, particularly valuable in the synthesis of antioxidant peptides and thiol-based redox modulators. Its tert-butylthio substitution provides enhanced stability compared to native cysteine, making it useful for studying protein thiolation and disulfide bond formation (Journal of Biological Chemistry). In medicinal chemistry, S-(tert-butylthio)-L-cysteine functions as a building block for creating bioactive molecules, including certain antiviral agents and enzyme inhibitors, where its thiol and amino acid backbone facilitate selective targeting of biological pathways (Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters). Additionally, the compound finds application in the development of fluorescent probes for bioimaging, where its thiol group allows for selective labeling of biological targets such as proteins and nucleic acids (Analytical Chemistry). It is also employed in the synthesis of certain agrochemicals, though specific applications in this area are limited to non-agricultural research settings (Pest Management Science).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review