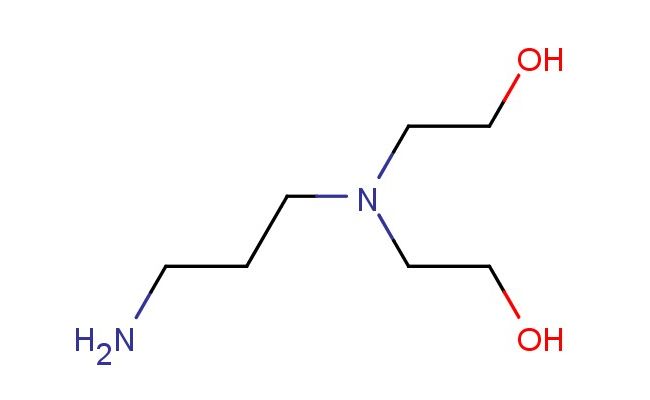
N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine
$300.00
CAS No.: 4985-85-7
Catalog No.: 195017
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H18N2O2
MW: 162.233
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NCCCN(CCO)CCO
Catalog No.: 195017
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H18N2O2
MW: 162.233
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NCCCN(CCO)CCO
N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine; CAS No.: 4985-85-7; N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine. PROPERTIES: N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine appears as a colorless to pale yellow, hygroscopic liquid with a slight amine odor. Its molecular formula is C8H19NO3, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 181.24 g/mol. The compound exhibits a boiling point around 250-255 C at 760 mmHg and a density of about 1.05 g/cm? at 25 C. It demonstrates high solubility in water and is miscible with most polar organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol. The substance is strongly hygroscopic and should be protected from exposure to atmospheric moisture. Proper storage requires keeping it in a tightly sealed container, preferably under an inert atmosphere like nitrogen, in a cool and dry environment at temperatures below 25 C. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective equipment as the compound may cause severe skin burns and eye damage. Inhalation of vapors may lead to respiratory tract irritation. In case of exposure, immediate rinsing with water and emergency medical treatment is essential. The substance is classified as corrosive (GHS classification). APPLICATIONS: N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine functions as a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of surfactants and emulsifiers, where its amine and hydroxyl groups enable the creation of non-ionic and cationic surfactants with excellent wetting and dispersing properties (Journal of Surfactants and Detergents). In chemical analysis, N-(3-aminopropyl)diethanolamine serves as a chelating agent for metal ions, forming stable complexes with transition metals for separation and quantification purposes (Analytical Chemistry). Additionally, it finds application in the preparation of corrosion inhibitors for metal surfaces, where its amine groups adsorb onto metal substrates to prevent oxidation and degradation (Corrosion Science). The compound is also employed in the synthesis of epoxy curing agents and resin modifiers, where its reactive amine functionality reacts with epoxy groups to form thermoset polymers with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties (Journal of Applied Polymer Science).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review