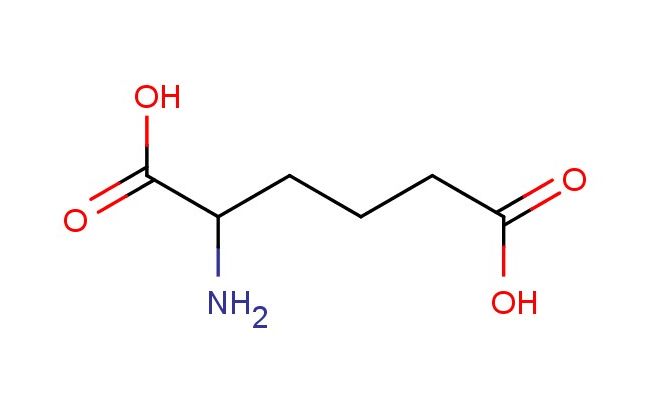
2-aminohexanedioic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 542-32-5
Catalog No.: 196727
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H11NO4
MW: 161.157
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC(C(=O)O)CCCC(=O)O
Catalog No.: 196727
Purity: 95%
MF: C6H11NO4
MW: 161.157
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC(C(=O)O)CCCC(=O)O
2-aminohexanedioic acid; CAS No.: 542-32-5; 2-aminohexanedioic acid. PROPERTIES: This amino-substituted hexanedioic acid features molecular formula C?H??NO? with molecular weight 157.16 g/mol. It typically exists as a white crystalline powder. Soluble in polar protic solvents like methanol and water. Melting point approximately 150-155 C. Exhibits IR absorption for carboxylic acid (~2900-2500 cm??) and amine groups (~3300-3000 cm??). Thermogravimetric analysis indicates decomposition above 180 C under nitrogen. For optimal stability, 2-aminohexanedioic acid should be stored at 2-8 C in tightly sealed containers with desiccant, protected from light. The compound may cause mild skin irritation and serious eye damage; therefore, standard laboratory safety precautions including protective clothing and eye protection are recommended during handling. APPLICATIONS: As an amino-substituted hexanedioic acid, 2-aminohexanedioic acid is predominantly utilized in the synthesis of polyamino acid hydrogels. It serves as a key monomer for constructing hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties, where the amino and carboxylic acid groups form crosslinked networks via amidation reactions (Biomacromolecules). Additionally, the compound participates in the synthesis of peptide-based therapeutics, where its amino acid functionality enables conjugation to biomolecules via amide bond formation (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). In materials science, it functions as a monomer for preparing polyamide membranes with enhanced gas separation properties, where the amide groups contribute to selective permeability (Journal of Membrane Science). Furthermore, the compound serves as a starting material in the development of chiral ligands for asymmetric catalysis, where its amino acid structure provides valuable stereoinduction in transition metal complexes (Catalysis Science & Technology).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review