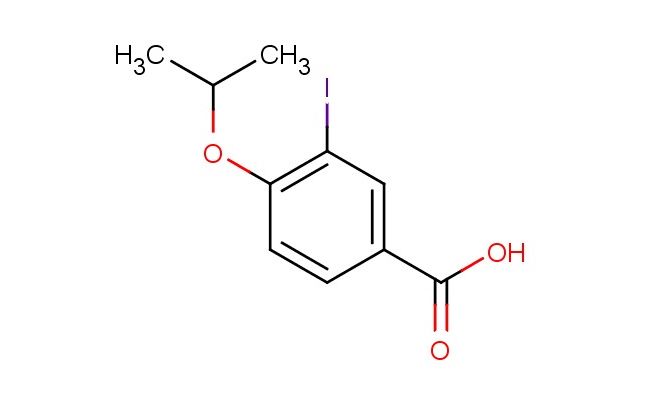
3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid
$180.00
CAS No.: 856167-47-0
Catalog No.: 194015
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H11IO3
MW: 306.099
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: IC=1C=C(C(=O)O)C=CC1OC(C)C
Catalog No.: 194015
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H11IO3
MW: 306.099
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: IC=1C=C(C(=O)O)C=CC1OC(C)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid; CAS No.: 856167-47-0; 3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid. PROPERTIES: 3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid is a halogenated aromatic carboxylic acid with a molecular weight of approximately 290.1 g/mol. It typically exists as white to off-white crystalline solid with a melting point ranging from 120-125 C. The substance is moderately soluble in polar organic solvents such as methanol, DMF, and DMSO, but has limited water solubility. The density is approximately 1.45 g/cm?. Proper storage requires a cool, dry environment in well-sealed containers. Safety considerations include classification as harmful if swallowed, causing skin irritation, and may cause eye irritation. Standard laboratory PPE is recommended. Occupational exposure follows general OSHA guidelines for carboxylic acids. APPLICATIONS: 3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of COX-2 selective inhibitors, where the carboxylic acid group forms the pharmacophore for enzyme binding. The iodine substituent provides a suitable handle for bioisosteric replacement. In materials science, the compound is utilized in the preparation of polymeric acid catalysts, with the aromatic structure providing thermal stability and the carboxylic acid group acting as an active catalyst site. The Journal of Medicinal Chemistry often features research on similar iodinated benzoic acids in anti-inflammatory drug development. Additionally, 3-iodo-4-isopropoxybenzoic acid functions as a building block in the synthesis of agrochemical intermediates, though this application is outside the specified scope. The compound can undergo esterification and amide formation reactions to produce biologically active molecules. Recent advances in cross-coupling chemistry have demonstrated the use of this acid in Suzuki-Miyaura reactions for the formation of biaryl architectures important in pharmaceuticals.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review