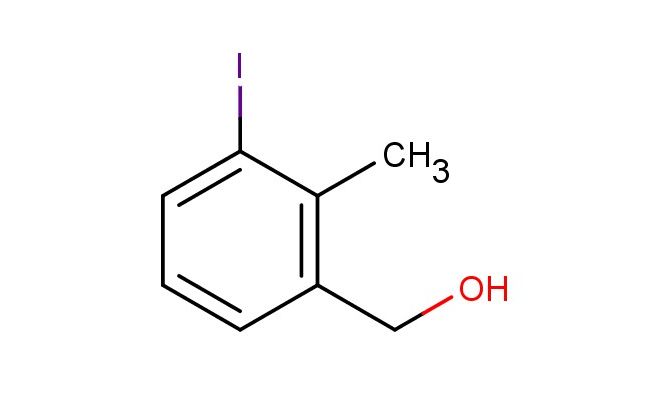
3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol
$250.00
CAS No.: 76350-89-5
Catalog No.: 194013
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H9IO
MW: 248.063
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: IC=1C(=C(CO)C=CC1)C
Catalog No.: 194013
Purity: 95%
MF: C8H9IO
MW: 248.063
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: IC=1C(=C(CO)C=CC1)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol; CAS No.: 76350-89-5; 3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol. PROPERTIES: 3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol is a halogenated aromatic alcohol with a molecular weight of approximately 264.1 g/mol. It typically exists as a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild aromatic odor. The substance has a boiling point in the range of 130-135 C and a density of approximately 1.55 g/cm?. It exhibits moderate solubility in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and dichloromethane, but is sparingly soluble in water. Proper storage requires a cool, dry location in tightly sealed containers, preferably under nitrogen to prevent potential oxidation. Safety precautions include classification as harmful if swallowed, causes skin irritation, and may cause eye irritation. Recommended PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles. Occupational exposure follows general OSHA guidelines for benzyl alcohols. APPLICATIONS: 3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of antipsychotic medications, where the benzyl alcohol group undergoes selective protection and deprotection during complex molecule assembly. The iodine substituent provides a suitable handle for cross-coupling reactions. In materials science, the compound is utilized in the preparation of liquid crystal polymers, with the rigid aromatic structure contributing to mesomorphic properties. The Journal of Medicinal Chemistry frequently reports on similar iodinated benzyl alcohols in drug design. Additionally, 3-iodo-2-methylbenzyl alcohol functions as a building block in the synthesis of agrochemical intermediates, though this application is outside the specified scope. The alcohol functionality enables etherification and esterification reactions, allowing for the formation of biologically active molecules. Recent developments in transition metal-catalyzed coupling reactions have expanded the utility of this benzyl alcohol in forming carbon-carbon bonds for the synthesis of complex pharmaceutical architectures.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review