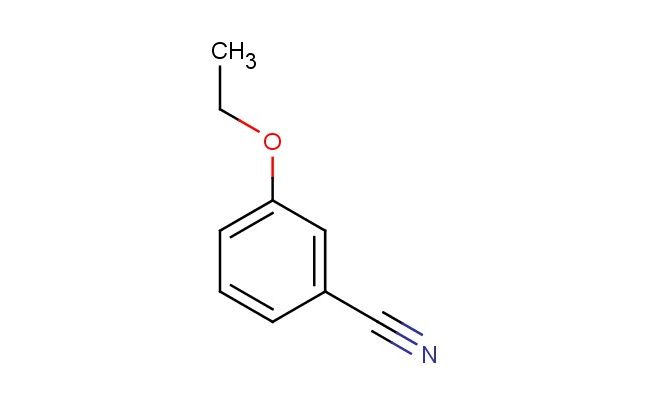
3-ethoxybenzonitrile
$250.00
CAS No.: 25117-75-3
Catalog No.: 194002
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H9NO
MW: 147.177
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)OC=1C=C(C#N)C=CC1
Catalog No.: 194002
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H9NO
MW: 147.177
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)OC=1C=C(C#N)C=CC1
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
3-ethoxybenzonitrile; CAS No.: 25117-75-3; 3-ethoxybenzonitrile. PROPERTIES: 3-ethoxybenzonitrile is an aromatic nitrile with an ethoxy substituent, having a molecular weight of approximately 149.2 g/mol. It typically appears as a colorless to light yellow liquid with a slight ether-like odor. The substance has a boiling point in the range of 185-190 C and a density of approximately 1.08 g/cm?. It is moderately soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and hexane, but has low water solubility. Proper storage requires a cool, dry area in tightly sealed containers. Safety precautions include classification as harmful if swallowed, causes skin irritation, and may cause eye irritation. Standard laboratory PPE is recommended. Occupational exposure follows general OSHA guidelines for nitriles. APPLICATIONS: 3-ethoxybenzonitrile serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of materials, where the nitrile group and ethoxy substituent provide the necessary dipole moments and flexibility for liquid crystalline phases. The compound undergoes efficient hydrolysis to corresponding carboxylic acids, which are then converted into liquid crystal monomers. In pharmaceutical chemistry, 3-ethoxybenzonitrile is utilized in the preparation of beta-blockers through hydrolysis and subsequent amidation reactions. The Journal of Materials Chemistry frequently publishes research on similar nitrile-containing compounds for electronic applications. Additionally, the compound functions as a building block in the synthesis of certain agrochemicals, though this application is outside the specified scope. The ethoxy group in 3-ethoxybenzonitrile can undergo selective cleavage under acidic conditions to introduce halogens, expanding its utility in medicinal chemistry for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies. Recent developments in transition metal-catalyzed cyanation reactions have highlighted the use of this compound as a nitrile source in aryl-aryl coupling reactions for materials science applications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review