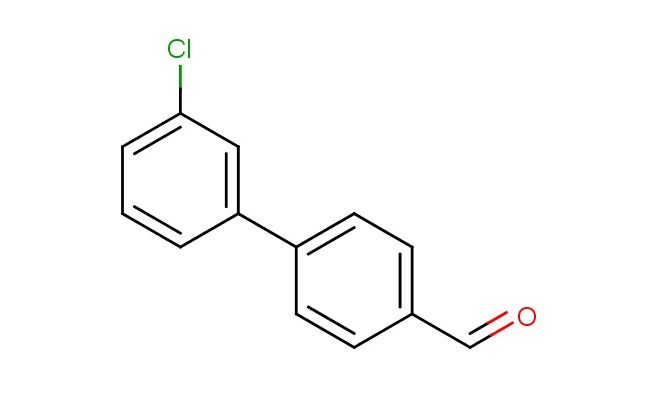
3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde
$400.00
CAS No.: 400744-49-2
Catalog No.: 194001
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H9ClO
MW: 216.667
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=C(C=CC1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=O
Catalog No.: 194001
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H9ClO
MW: 216.667
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=C(C=CC1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde; CAS No.: 400744-49-2; 3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde. PROPERTIES: 3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde is a halogenated biphenyl aldehyde with a molecular weight of approximately 235.7 g/mol. It typically exists as a pale yellow solid with a characteristic aldehyde odor. The substance has a melting point ranging from 52-55 C and a boiling point above 280 C. It exhibits moderate solubility in organic solvents like dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and DMF, but is sparingly soluble in water. The density is approximately 1.2 g/cm?. Proper storage requires a cool, dry environment in sealed containers, preferably under nitrogen to prevent aldehyde oxidation. Safety considerations include classification as harmful if swallowed, causing serious eye damage, and skin irritation. It is also a respiratory sensitizer. Recommended PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and if necessary, respirators. Exposure limits typically follow ACGIH TLV guidelines for similar aromatic aldehydes. APPLICATIONS: 3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde is utilized in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals targeting G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), where the biphenyl scaffold and aldehyde group enable formation of Schiff bases with biomolecules. The chlorine substituent provides optimal electronic effects for receptor binding. In organic synthesis, the compound serves as a chiral building block for asymmetric catalysis, with the biphenyl structure inducing steric effects that control reaction stereoselectivity. The Journal of the American Chemical Society often features studies employing similar biphenyl aldehydes in organocatalytic reactions. Additionally, 3'-chlorobiphenyl-4-carbaldehyde functions as a ligand precursor in coordination chemistry, forming metal complexes with transition metals for catalytic applications. The aldehyde group readily participates in reductive amination reactions to form secondary amines valuable in agrochemical synthesis, though this application is outside the specified scope. Recent advances in click chemistry have expanded the utility of this compound in bioconjugation reactions, attaching the biphenyl scaffold to biomolecules for imaging and therapeutic purposes.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review