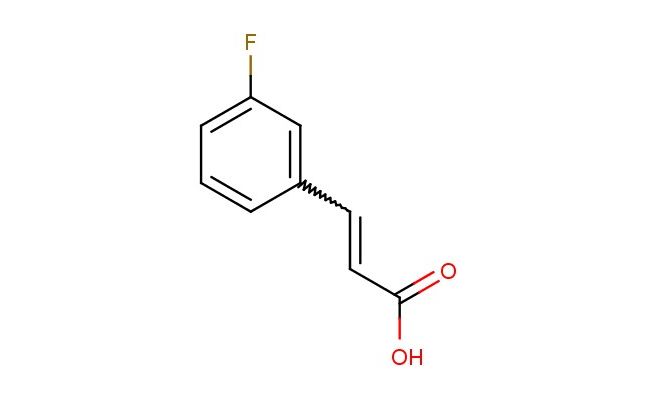
3-(3-fluorophenyl)acrylic acid
$250.00
CAS No.: 458-46-8
Catalog No.: WLZ1213
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7FO2
MW: 166.151
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC=1C=C(C=CC(=O)O)C=CC1
Catalog No.: WLZ1213
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7FO2
MW: 166.151
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC=1C=C(C=CC(=O)O)C=CC1
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 458-46-8; 3-(3-fluorophenyl)acrylic acid. PROPERTIES: This , -unsaturated carboxylic acid features a fluorine-substituted phenyl group conjugated to a carbon-carbon double bond, creating a molecule with potential applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science. The 3-(3-fluorophenyl)acrylic acid typically presents as a white to off-white crystalline powder with limited aqueous solubility but good solubility in common organic solvents. Its molecular structure includes a conjugated system between the phenyl ring and acrylic acid moiety, which contributes to its characteristic absorption in the ultraviolet region. For optimal stability and to preserve its double bond integrity, this compound should be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in an amber glass bottle under an inert atmosphere. When handling, chemists should wear appropriate personal protective equipment including nitrile gloves and safety goggles. This compound is sensitive to light and may undergo polymerization upon exposure to UV radiation. In case of skin contact, wash immediately with soap and water; if eye contact occurs, rinse thoroughly and seek medical evaluation. APPLICATIONS: The 3-(3-fluorophenyl)acrylic acid serves as a valuable building block in pharmaceutical research, particularly for developing kinase inhibitors and other small molecule therapeutics. The fluorinated phenyl group provides a bioisosteric replacement for hydrogen, potentially improving metabolic stability and target binding affinity. In materials science, this compound functions as a monomer for creating polymers with specific optical and electronic properties. Additionally, the molecule finds utility in organic synthesis as a Michael acceptor for nucleophilic addition reactions, enabling the creation of complex molecular architectures. Researchers utilizing this compound can leverage its electronic and steric properties to advance investigations into drug discovery and advanced materials development.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review