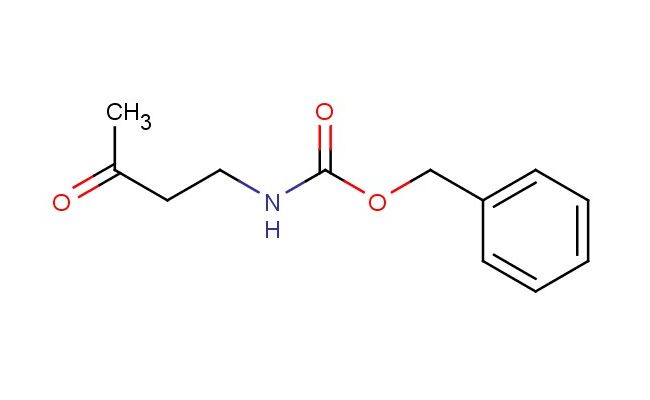
benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate
$250.00
CAS No.: 95484-17-6
Catalog No.: 193157
Purity: 95%
MF: C12H15NO3
MW: 221.256
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C(CCNC(OCC1=CC=CC=C1)=O)C
Catalog No.: 193157
Purity: 95%
MF: C12H15NO3
MW: 221.256
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C(CCNC(OCC1=CC=CC=C1)=O)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate; CAS No.: 95484-17-6 benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate. PROPERTIES: benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a molecular weight of 243.3 g/mol. It has a boiling point around 150-155 C at reduced pressure and a density of approximately 1.1 g/cm?. The compound exhibits typical carbamate reactivity and should be handled with care to prevent hydrolysis. When working with benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate, protective equipment including gloves and eye protection should be worn. Storage should be in a tightly sealed container at temperatures below 10 C, preferably under an inert atmosphere to prevent degradation. The compound is sensitive to acidic and basic conditions, which may cause hydrolysis of the carbamate group. APPLICATIONS: benzyl 3-oxobutylcarbamate serves as a protected amine intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and advanced materials. Its oxo group provides a useful handle for reduction to alcohol or participation in conjugate addition reactions, as demonstrated in Organic Syntheses. Derivatives of this compound have been explored in the development of kinase inhibitors and other targeted therapeutics, as reported in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. The benzyl protection provides a convenient handle for further functionalization in synthetic sequences. Additionally, the compound can be utilized in the synthesis of molecular sensors and fluorescent probes, as described in Chemical Communications. The combination of the benzyl and carbamate protections makes this compound particularly useful in solid-phase synthesis and the preparation of combinatorial libraries for drug discovery, as highlighted in the Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry. The oxo functionality also makes it suitable for use in organic electronics as a building block for semiconducting polymers, as noted in Advanced Materials.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review