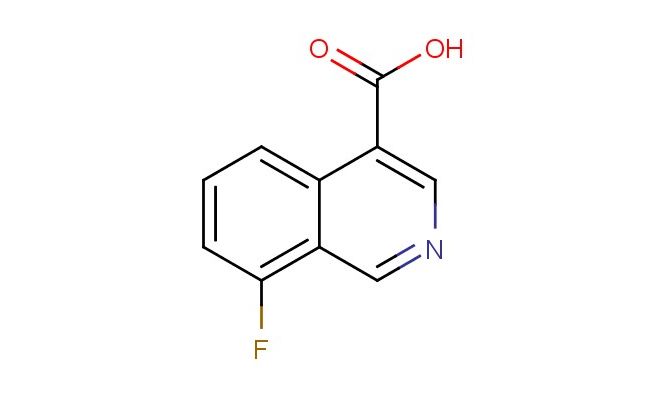
8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid
$550.00
CAS No.: 1824276-14-3
Catalog No.: 191944
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6FNO2
MW: 191.161
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC=1C=CC=C2C(=CN=CC12)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 191944
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H6FNO2
MW: 191.161
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC=1C=CC=C2C(=CN=CC12)C(=O)O
8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 1824276-14-3; 8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid (CAS No.: 1824276-14-3) is a heterocyclic compound featuring a fluorine atom at the 8-position and a carboxylic acid group at the 4-position of the isoquinoline nucleus. This white to off-white crystalline solid exhibits typical carboxylic acid characteristics with a pKa value around 3.2, making it relatively acidic. The compound demonstrates moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide, while being sparingly soluble in water due to its hydrophobic fluorine substituent. Its melting point ranges between 215-218 C, requiring careful handling to prevent decomposition. For long-term storage, 8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid should be kept in a tightly sealed container under nitrogen atmosphere at 2-8 C, protected from moisture and light. Safety precautions include wearing N95 respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and safety goggles to prevent skin and eye contact, as the compound may cause mild irritation. The flash point exceeds 100 C, but closed system operations are recommended to minimize dust exposure. APPLICATIONS: 8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid serves as a versatile intermediate in medicinal chemistry, particularly in the synthesis of kinase inhibitors as reported in oncology research. Its isoquinoline scaffold provides structural flexibility for bioisosteric replacements in drug discovery programs. In materials science, the compound contributes to the development of organic semiconductors due to its electron-withdrawing fluorine substituent, as documented in polymer chemistry literature. Additionally, 8-fluoroisoquinoline-4-carboxylic acid functions as a building block for fluorescent probes used in bioimaging applications, with several studies highlighting its utility in monitoring intracellular pH changes through fluorescence resonance energy transfer mechanisms.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review