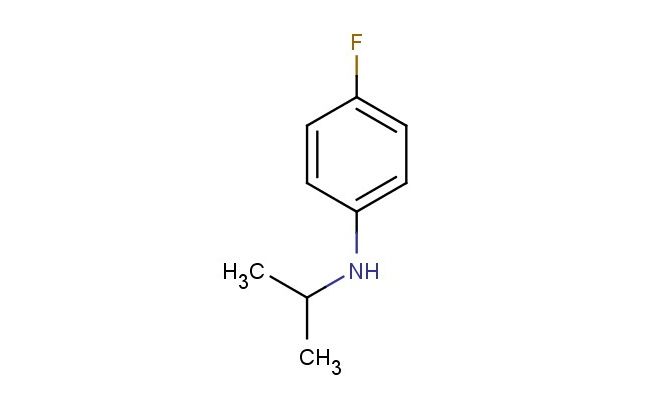
4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline
$365.00
CAS No.: 70441-63-3
Catalog No.: 195021
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H12FN
MW: 153.2
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=CC=C(NC(C)C)C=C1
Catalog No.: 195021
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H12FN
MW: 153.2
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: FC1=CC=C(NC(C)C)C=C1
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline; CAS No.: 70441-63-3; 4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline. PROPERTIES: 4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a characteristic aromatic amine odor. Its molecular formula is C9H11FNN, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 166.19 g/mol. The compound exhibits a boiling point around 180-185 C at 760 mmHg and a density of about 1.02 g/cm? at 25 C. It demonstrates moderate solubility in water and is miscible with common organic solvents such as ether, chloroform, and tetrahydrofuran. The substance is sensitive to oxidation and may form explosive peroxides upon prolonged storage. Proper storage requires keeping it in a tightly sealed, amber glass container with a suitable stabilizer, in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The temperature should be maintained below 10 C if possible. Safety precautions include using chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats to prevent skin absorption and inhalation of vapors. The compound may cause severe skin burns and eye damage, and accidental ingestion may be fatal. In case of exposure, immediate rinsing with water and emergency medical treatment is essential. The substance is classified as toxic and corrosive (GHS classification). APPLICATIONS: 4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline functions as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of liquid crystal materials, where its fluorinated aromatic amine structure contributes to mesomorphic properties and alignment characteristics (Journal of Fluorine Chemistry). In pharmaceutical research, 4-fluoro-N-isopropylaniline serves as a building block for creating bioactive molecules, including certain antidepressants and antipsychotics, through its ability to participate in Suzuki-Miyaura couplings and other cross-coupling reactions (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). Additionally, it finds application in the preparation of certain agrochemicals, though specific applications in this area are limited to non-agricultural research settings (Pest Management Science). The compound is also employed in materials science as a monomer for creating polyimides and other high-performance polymers with enhanced thermal stability and mechanical properties, leveraging its fluorine substituent to impart desirable characteristics (Polymer International).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review