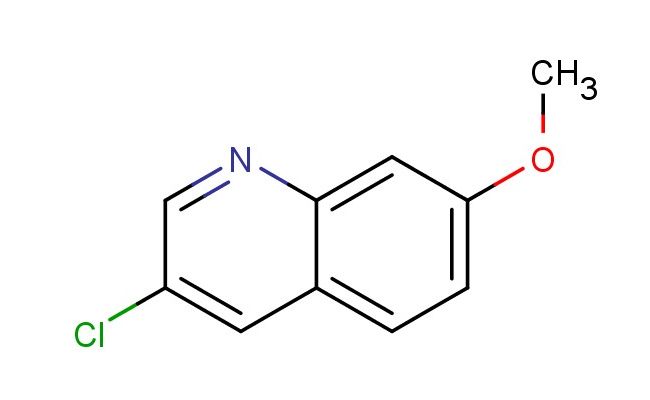
3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline
$200.00
CAS No.: 858279-19-3
Catalog No.: 191984
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H8ClNO
MW: 193.633
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=NC2=CC(=CC=C2C1)OC
Catalog No.: 191984
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H8ClNO
MW: 193.633
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C=NC2=CC(=CC=C2C1)OC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline; CAS No.: 858279-19-3;3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline. PROPERTIES: 3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline is a halogenated quinoline ether with molecular formula C10H7ClNO. This crystalline compound typically appears as colorless needles and has a melting point between 75-80 C. The molecule features a quinoline core with a chlorine atom at position 3 and a methoxy group at position 7. The 3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline exhibits moderate basic character due to the quinoline nitrogen, with a pKa value around 4.2 for the conjugate acid. It shows good solubility in common organic solvents like dichloromethane and moderate solubility in water. Proper storage requires maintaining in a tightly sealed container with appropriate drying agents, stored below 20 C to prevent hydrolytic degradation. Safety measures include using chemical splash goggles and acid-resistant gloves, as the compound can cause serious eye damage and skin corrosion. It is classified under GHS with H314 and H318 hazard statements for causing severe skin burns and eye damage. APPLICATIONS: The 3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline structure functions as a key intermediate in the synthesis of quinoline-based antimalarial agents, as reported in medicinal chemistry research focusing on tropical disease treatments. The chloro and methoxy substituents provide a site for further functionalization via nucleophilic substitution and coupling reactions. Additionally, 3-chloro-7-methoxyquinoline derivatives have been explored in materials science for creating electroactive molecules with interesting optical properties, as described in chemical physics publications. The compound's ability to form coordination complexes with metal ions has also made it useful in developing chemical sensors for metal detection, as documented in analytical chemistry studies emphasizing selective ion recognition.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review