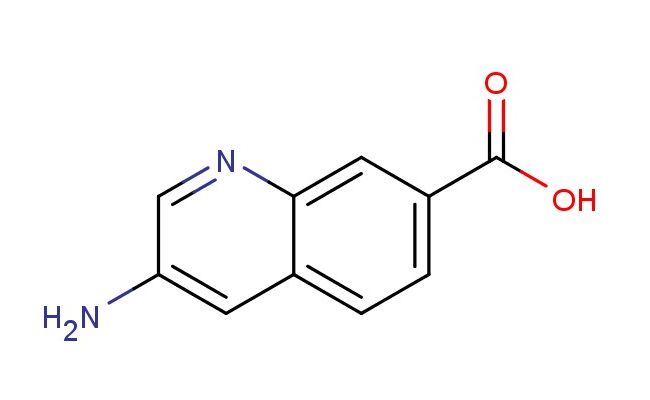
3-aminoquinoline-7-carboxylic acid
$450.00
CAS No.: 1824051-45-7
Catalog No.: 191949
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H8N2O2
MW: 188.186
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C=NC2=CC(=CC=C2C1)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 191949
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H8N2O2
MW: 188.186
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC=1C=NC2=CC(=CC=C2C1)C(=O)O
3-aminoquinoline-7-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 1824051-45-7; 3-aminoquinoline-7-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 3-aminoquinoline-7-carboxylic acid (CAS No.: 1824051-45-7) appears as a pale yellow crystalline solid with a melting point between 220-223 C. The compound features an amino group at position 3 and a carboxylic acid at position 7 of the quinoline ring system, exhibiting dual functionality that imparts distinct chemical reactivity. Its carboxylic acid group demonstrates typical acidity with a pKa around 3.7, while the amino group shows moderate basicity (pKa ~5.5). Solubility characteristics reveal good dissolvability in polar solvents like methanol and DMF, with limited water solubility due to the hydrophobic aromatic system. The substance is hygroscopic and sensitive to light, necessitating storage in a tightly sealed amber container under nitrogen atmosphere at controlled temperature (15-25 C). Safety protocols recommend N95 respiratory protection, nitrile gloves, and safety goggles due to potential skin irritation and eye damage. The compound has a relatively high flash point (>100 C) but generates dust that may form explosive mixtures with air. APPLICATIONS: 3-aminoquinoline-7-carboxylic acid functions as a critical intermediate in synthesizing anticancer agents targeting tyrosine kinases as documented in oncology research. Its quinoline scaffold enables the development of antibacterial agents with activity against drug-resistant pathogens as reported in pharmaceutical chemistry literature. Additionally, 1824051-45-7 serves as a building block for fluorescent DNA intercalators used in genetic research, with several studies highlighting its role in creating sequence-specific DNA binding agents for molecular biology applications. The compound also contributes to the synthesis of agrochemical intermediates for developing fungicides with novel modes of action, as described in agricultural chemistry literature.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review