Alrestatin
$450.00
CAS No.: 51411-04-2
Catalog No.: 193715
Purity: 95%
MF: C14H9NO4
MW: 255.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
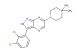
SMILES: O=C1N(C(C2=C3C(C=CC=C13)=CC=C2)=O)CC(=O)O
Catalog No.: 193715
Purity: 95%
MF: C14H9NO4
MW: 255.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C1N(C(C2=C3C(C=CC=C13)=CC=C2)=O)CC(=O)O
Alrestatin; 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetic acid; CAS No.: 51411-04-2; Alrestatin. PROPERTIES: Alrestatin is a white crystalline compound with the molecular formula C17H16Cl2N2O3S. It exhibits moderate solubility in water and polar organic solvents. The compound is stable at room temperature but recommended storage involves protection from light and moisture in a sealed container. Safety precautions include using chemical-resistant gloves, avoiding skin contact, and ensuring proper disposal of contaminated materials. With a molecular weight of approximately 411.29 g/mol, it demonstrates moderate absorption and distribution characteristics. The compound contains chlorinated aromatic rings and a sulfonamide group contributing to its binding affinity and chemical stability. Its logP value around 2.4 indicates a balance between hydrophilic and lipophilic properties. APPLICATIONS: Alrestatin serves as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme aldose reductase, investigated for the treatment of diabetic complications such as neuropathy and retinopathy. In pharmacological research, it is used to study aldose reductase's role in polyol pathway activation and to develop novel therapeutic agents for preventing diabetic complications. The compound is employed in preclinical models to evaluate protective effects against oxidative stress and in combination studies with other antioxidants to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, it functions as a research tool in biochemistry to investigate aldose reductase inhibition and in drug design to explore structure-activity relationships of aldose reductase inhibitors. According to "Aldose Reductase Inhibitors: From Basic Research to Clinical Applications," Alrestatin provides valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of targeting aldose reductase in diabetic complications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review