NHPI-PEG4-C2-NHS ester
$300.00
CAS No.: 1415328-95-8
Catalog No.: 198478
Purity: 95%
MF: C23H28N2O11
MW: 508.48
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
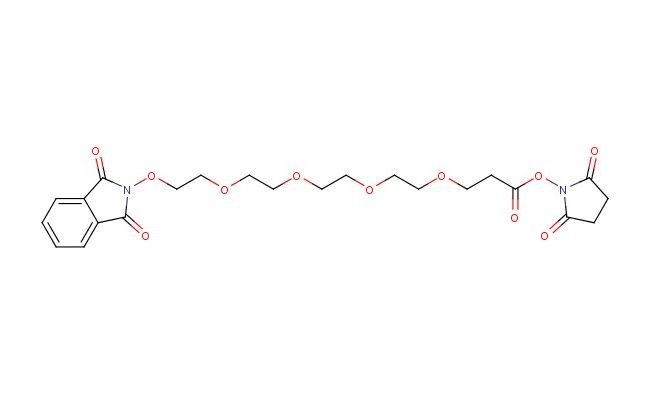
SMILES: O=C1N(C(C2=CC=CC=C12)=O)OCCOCCOCCOCCOCCC(=O)ON1C(CCC1=O)=O
Catalog No.: 198478
Purity: 95%
MF: C23H28N2O11
MW: 508.48
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C1N(C(C2=CC=CC=C12)=O)OCCOCCOCCOCCOCCC(=O)ON1C(CCC1=O)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS No.: 1415328-95-8; NHPI-PEG4-C2-NHS ester. PROPERTIES: NHPI-PEG4-C2-NHS ester is a PEGylated crosslinking agent with molecular formula C19H32N3O9P and molecular weight 497.47 g/mol. It typically exists as a white powder with good solubility in dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. The compound is sensitive to moisture and should be stored at -20 C in a tightly sealed container under inert atmosphere. Safety considerations include potential for causing eye irritation, requiring safety goggles during handling. APPLICATIONS: In bioconjugation chemistry, NHPI-PEG4-C2-NHS ester serves as a PEGylation agent that introduces a PEG chain terminated with an aminohexanoyl group. The NHS ester reacts with primary amines on proteins, antibodies, or peptides, facilitating controlled PEGylation to improve solubility and reduce immunogenicity. In pharmaceutical research, the compound is used to develop PEGylated therapeutics with enhanced pharmacokinetic properties. The PEG4 chain provides sufficient distance between the biomolecule and the reactive group to minimize steric hindrance. Additionally, the NHPICAS No.: 13171-93-2; Z-Gly-Gly-Phe-OH. PROPERTIES: Z-Gly-Gly-Phe-OH is a protected tripeptide with molecular formula C19H23NO6 and molecular weight 357.39 g/mol. It typically exists as a white to off-white powder with limited aqueous solubility, requiring dimethylformamide or dimethyl sulfoxide for dissolution. The compound is sensitive to acid and should be stored at room temperature in a tightly sealed container. Safety considerations include potential for causing skin and eye irritation, requiring protective gloves and eye protection during handling. APPLICATIONS: In peptide synthesis, Z-Gly-Gly-Phe-OH serves as a building block for assembling larger peptides. The benzyloxycarbonyl (Z) group protects the N-terminus of the glycine residue during solid-phase or solution-phase synthesis. In medicinal chemistry, the tripeptide is used to develop bioactive molecules that mimic natural peptide sequences or to create prodrugs that become activated upon removal of the protecting group. The Gly-Gly-Phe sequence is found in various signaling peptides and can be incorporated into drug candidates targeting specific receptors or enzymes. In biochemistry, the compound is used to study protease specificity and activity by serving as a substrate or inhibitor. The Z-protecting group allows controlled deprotection to release the active peptide sequence under specific conditions. Additionally, the tripeptide is utilized in materials science to create peptide-based materials with defined sequences that influence material properties such as self-assembly or biocompatibility. In chemical biology, Z-Gly-Gly-Phe-OH facilitates study of peptide-receptor interactions and the development of targeted delivery systems where the peptide sequence directs cargo to specific cell types. (Peptide synthesis protocols and medicinal chemistry literature)
Reviews
Write Your Own Review